For Finalizing the Mesh, use
Free Quad to remesh one or several faces. The operation separates the selected boundaries from the mesh, creates geometry from the separated mesh, meshes the geometry, and then copies the new generated mesh onto the original mesh. This operation has the following practical implications:
To scale the geometry during the meshing operation, change the x-scale,
y-scale, and
z-scale in 3D to positive real numbers. If any of the scale factors are not equal to one, the software scales the geometry in those directions before meshing; after meshing, it restores the geometry and mesh to fit the original size, as shown in
Figure 8-37.
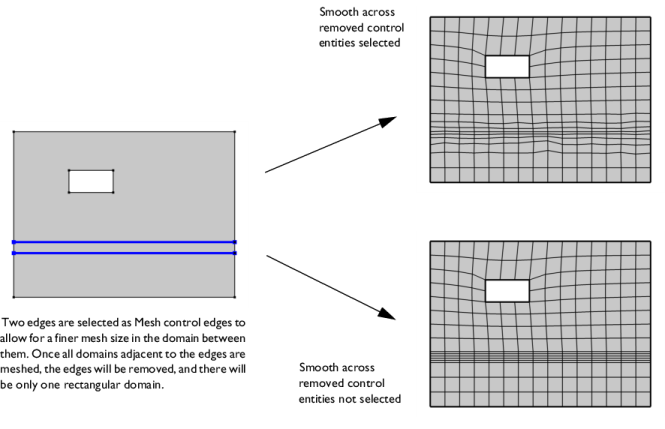
Select the Smooth across removed control entities check box to smooth the transition in element size across removed
Controlling the Mesh Size Using Mesh Control Entities. You can specify the number of smoothing iterations in the
Number of iterations field. In the
Maximum element depth to process field you can specify the maximum element depth for the mesh points to be smoothed.
From the Method list, choose the tessellation method to use for generating an unstructured quadrilateral mesh:
The Relative simplification tolerance (default value: 0.01) is relative to the dimensions of the entire geometry and specifies a global limit for how much the mesh can be modified. The
Defect removal factor (default value: 1) is relative to the local feature size, as estimated by the algorithm, and is combined with the global limit to produce a limit for how much the mesh can be modified at a certain location. If the mesh contains many defects that you want to remove, you could try to increase the value of the
Defect removal factor. If the mesh describes the desired geometry with high accuracy, you may want to decrease this factor instead.