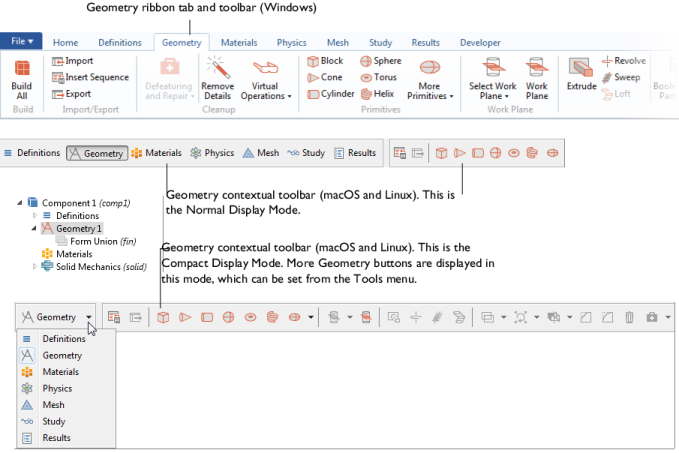
After a Component node is added to the model, the
Geometry ribbon toolbar (Windows) or the
Geometry contextual toolbar (macOS and Linux) is made accessible (
Geometry Toolbar). Click the
Geometry toolbar to display the options.
Options become available based on where in the geometry you are working. As in Figure 7-1, the
Geometry toolbar has some options grayed out because these are not yet available. As a geometry sequence is built, and you select geometry objects in the
Graphics window, the applicable options become available.
When one of the buttons is clicked, COMSOL Multiphysics performs the associated operation on the selected objects and creates the resulting objects, often adding a node to the geometry sequence. If you want to modify the operation, you can edit and rebuild this node. See
About Highlighted Geometric Entities in the Graphics Window for details.
In 2D and 1D, there are buttons for drawing Geometric Primitives using the mouse. In 3D, the buttons are available to create primitives, but you cannot draw these using the mouse. See
Geometry Toolbar and
Table 2-8 for a list of the buttons and links to the individual features.
For Windows users, the COMSOL Desktop displays the current x and
y coordinates at the bottom of the desktop when you move the cursor in the Graphics window when working with the geometry. Also, when you interactively create 2D geometric primitives, the display shows the current dimensions for the following geometric primitives:
For 2D geometries, you can click the Edit button (

) in the
Graphics window’s toolbar to enter an Edit selection mode, where you can perform the following actions:
Use the Edit Object (

) node to adjust the edges and vertices for a 2D geometry object or to add or delete edges and vertices in the object. In the
Model Builder, right-click a 2D
Geometry and select
Edit Object.
The Edit Object function can also be started using the
Edit Object button (

) in the Geometry toolbar: