|
1
|
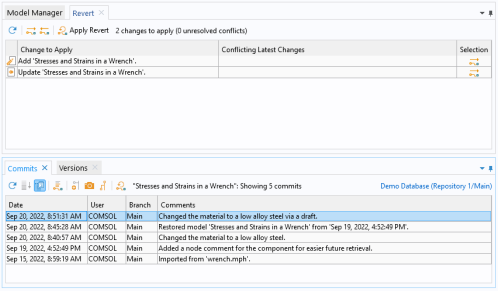
Right-click the Stresses and Strains in a Wrench regular model (
|

|
2
|
Select the top table row and click the Commit Details button (
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Click the Refresh button (
|
|
5
|
Right-click the regular model and select Versions (
|
|
1
|
Right-click the Stresses and Strains in a Wrench draft model (
|
|
2
|
Click OK to delete the draft.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Click the Show More button (
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
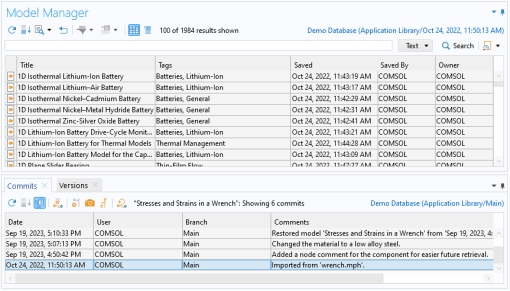
Right-click the table row with the comment Changed the material to a low alloy steel in the Commits window and select Search in Commit (
|
|
1
|
Click the link button in the upper-right corner in the Model Manager window — you will find it above the Search button (
|
|
2
|
Select the Main branch node (
|
|
3
|
Click OK.
|
|
2
|
Under Snapshots (
|
|
3
|
Click OK.
|