and an elliptic blending function, α, which is used to combine near-wall effects with those in the far-field. The complete model for compressible flow reads,
Realizability Constraints are applied to the turbulent viscosity.
The wall distance variable, lw, is provided by a mathematical Wall Distance interface that is included when using the v2-f
model. The solution to the wall distance equation is controlled using the parameter
lref. The distance to objects larger than
lref is represented accurately, while objects smaller than
lref are effectively diminished by appearing to be farther away than they actually are. This is a desirable feature in turbulence modeling since small objects would get too large an impact on the solution if the wall distance were measured exactly.
δw is the distance to the closest wall. The boundary conditions for the momentum equations are a no-penetration condition
u ⋅ n = 0 and a shear stress condition
Here, κv, is the von Kármán constant (default value 0.41),
U|| is the velocity parallel to the wall, and
B is a constant that by default is set to 5.2.
These expression can be combined with the lift-off concept shown in Figure 3-7 which gives
δw = hw/2. The
k-equation formally fulfills
∇k ⋅ n = 0 both at the wall and in the log-layer, so this condition is applied for all
δw+.
The conditions for the turbulent dissipation rate, ε, is similar to that in the Wolfshtein model which is commonly employed in two-layer
k-
ε implementations (
Ref. 13):
The resulting wall resolution, δw+, is available as the postprocessing variable
Delta_wPlus.
Since all velocities must disappear on the wall, so must k and
ζ (since
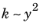
and
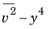
). Hence,
k = 0 and
ζ = 0 on the wall. By definition,
α = 0 on the wall.
where n is the wall normal direction. This condition is however numerically very unstable. Therefore,
ε is not solved for in the cells adjacent to a solid wall and instead the analytical relation
is prescribed in those cells (using the variable εw, which only exists in those cells).
Equation 3-152 can be derived as the first term in a series expansion of
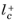 is the distance, measured in viscous units, from the wall to the center of the wall adjacent cell. The boundary variable Distance to cell center in viscous units
is the distance, measured in viscous units, from the wall to the center of the wall adjacent cell. The boundary variable Distance to cell center in viscous units,
lplus_cc, is available to ensure that the mesh is fine enough. Observe that it is unlikely that a solution is obtained at all if
The guidelines given in Inlet Values for the Turbulence Length Scale and Turbulent Intensity for selecting the turbulence length scale,
LT, and the turbulence intensity,
IT, apply also to the v2-f model.
The v2-f model has the same default initial guess as the standard k-
ε model (see
Initial Values) but with
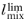
replaced by
lref. The default initial values for
ζ and
α are
2/3 and
1 respectively.