The operation removes selected faces that are isolated or are located between two domains by ignoring them. Composite domains are formed which may simplify meshing the geometry, for example if narrow domain regions are avoided.
An alternative is to use the Form Composite Domains operation. The
Remove Details operation provides a fully automated way to find and remove thin and small domains by ignoring faces.
To use the operation, in the Geometry toolbar, from the
Virtual Operations menu (

), select
Ignore Faces (

). Then enter the properties of the operation using the following sections:
Select the faces that you want to ignore in the Graphics window. They then appear in the
Faces to ignore list. If the geometry sequence includes user-defined selections above the
Ignore Faces node, choose
Manual to select faces, or choose one of the selection nodes from the list next to
Faces to ignore.
Click the Active button to toggle between turning ON and OFF the
Faces to ignore selections.
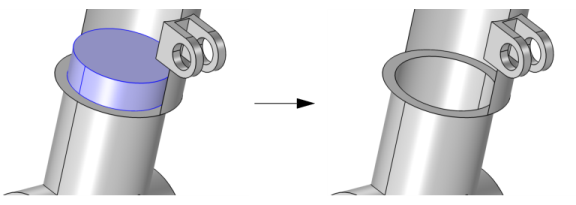
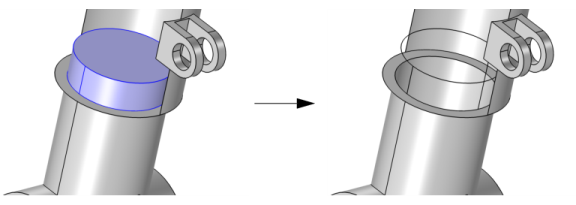
Use the Ignore adjacent vertices and edges check box to also remove the ignorable vertices and edges adjacent to the faces. Clearing the check box still removes the faces, but keeps the vertices and edges adjacent to the ignored faces, as shown below.
Use the Keep input for mesh control check box to specify that the selected faces disappear from the geometry but become available when you build the mesh. You can, for example, use a
mesh control face to partition the geometry to make it possible to sweep a hexahedral mesh. See also
Mesh Control Faces.

