Far Field plots are used to plot the value of a global variable for the far field of an electromagnetic field or acoustic pressure field.
The main advantage with the Far Field plot, as compared to making a Line Graph, is that the circle or sphere used for defining the plot directions is not part of the geometry for the solution. Thus, the number of plotting directions is decoupled from the discretization of the solution domain.
For the standard settings, see Expressions and Predefined Quantities. In 3D, you can also select the
Threshold check box and then enter a threshold value as a scalar number in the associated edit field. The threshold value corresponds to the evaluated radius that maps to the plotted radius 0. The default, if the
Threshold check box is cleared, is the minimum radius among those evaluated for. Additionally, in 3D, select the
Use as color expression check box to use the far-field plot expression defined in this section also as the color expression. The
Color section is then not available.
Select a Restriction:
None (the default) or
Manual. If
Manual is selected, enter values (SI unit: deg) for
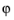 start
start (the default is 0 degrees) and
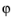 range
range (the default is 360 degrees). If you want to compute the beam width, select
On from the
Compute beam width list. Then, a
Level down field appears, where you can specify a nonnegative number to compute the beam width at a certain level down from the reference direction. The unit for that level is the same as the unit for the expression used in the far-field plot (dB, for example, for a far-field sound pressure level). The beam width is the width of the lobe around the reference direction (in degrees). When you compute the beam width, the computed values appear in a
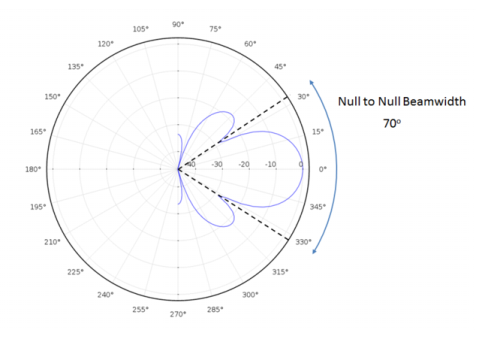
Beam width table with columns for the parameter (typically a frequency), the beam width, and the null-to-null beam width (the angular separation from which the magnitude of the radiation pattern decreases to zero away from the main beam; see the figure below).
For 1D Far Field plot nodes referring to a solution in a 2D axisymmetric or 3D component, under Center enter the coordinate at the center of the evaluation circle. Under
Normal specify the normal to the circular slice of the far-field bulb. The defaults is {0, 0, 1} for the normal using 3D components and {0, 1, 0} for the normal using 2D axisymmetric components.
Under Reference direction specify a reference direction from which the angle is measured. The entered vector is projected onto the evaluation plane. The default is {1, 0, 0} for the reference direction using 3D components and {0, 0, 1} for the reference direction using 2D axisymmetric components.
A schematic of the evaluation circle is depicted in Figure 20-3. In 3D, you can preview the evaluation circle in the geometry by clicking the
Preview Evaluation Plane button at the bottom of the
Evaluation section. An example of the resulting plot is depicted in
Figure 20-4.
Under Angles, enter the
Number of elevation angles. The default is 10. Enter the
Number of azimuth angles. The default is 20.
Select a Restriction:
None (the default) or
Manual. If
None is selected in a 3D plot group, you can also select the
Compute directivity check box. If the
Compute directivity check box is selected, you can enter or select an expression for the directivity in the
Directivity expression field. The direction for the strongest radiation and the directivity value (also in dB) display in a
Directivity table window (see
The Table Window and Tables Node). So if, for example, you model a speaker that is located in an infinite baffle (and symmetry is used in the far-field calculation), then plot and evaluate the whole field to get the directivity.
If Manual is selected, enter values (SI unit: deg) for:
If a pressure acoustics interface is used in the component from which the data set is taken, you can also specify the following settings for a radius-dependent far-field expression. Under Sphere from the list, select
Unit sphere (the default) or
Manual. If
Manual is selected, enter values for the
x,
y, and
z coordinates at the center of the sphere (SI unit: m). The default is 0. Enter a
Radius (SI unit: m). The default is 1 m.
This section is available in 1D plot groups only. Select the Show legends check box to display the plotted expressions to the right of the plot. In plots where each line represents a certain time value, eigenvalue, or parameter value, these values are also displayed.
When Automatic is selected from the
Legends list (the default), the legend texts appear automatically. You can add a prefix or a suffix to the automatic legend text in the
Prefix and
Suffix fields. If
Manual is selected from the
Legends list, enter your own legend text into the table.
