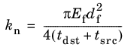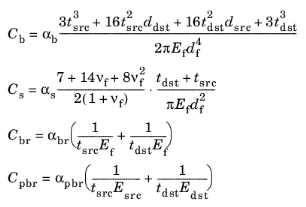When one or more Fasteners nodes are active in the model, five entries are added to the list of result templates:
|
•
|
A Fasteners Forces plot group that shows the normal and shear forces and a label showing the identity number of each fastener. Evaluate the Fasteners Normal Forces and Fasteners Shear Forces evaluation group to display the fasteners forces. The coloring can be affected by the addition of a Safety subnode.
|
|
•
|
A Fasteners Normal Forces evaluation group that contains a table of the location, normal forces, and damage index of all fasteners. Evaluate this table to display the forces in the Fasteners Forces plot group.
|
|
•
|
A Fasteners Shear Forces evaluation group that contains a table of the location, shear forces, and damage index of all fasteners. Evaluate this table to display the forces in the Fasteners Forces plot group.
|
|
•
|
A Fasteners Forces Magnitude evaluation group that contains a table of the normal and shear forces magnitude for all fasteners.
|
|
•
|
A Connected Region Indicator plot group that contains a line plot or a surface plot showing the hole edges or hole surrounding boundaries, respectively, on the destination surface where the fasteners are active. If there are other connection features in the Shell interface, all connection indicators appear in the same plots.
|
You must evaluate the Fasteners Normal Forces and Fasteners Shear Forces evaluation groups to update the Fasteners Forces plot group if you change the number of fasteners in your model or compute new results. Also, remove the Connected Region Indicator plot group and replace it by a new one if you change the hole selection type between edge or boundary.