For the Solution termination criterion: The
Segregated solver terminates after iteration
k if, for all the groups
j, the error estimate is smaller than the specified tolerance,
The number tol is the
Relative tolerance specified in the parent
Stationary Solver or
Time-Dependent Solver multiplied by the
Tolerance factor specified in the
Segregated solver. The error estimate in segregated iteration
k considers both updates done in the individual segregated groups and the total solution change relative to iteration
k − 1,
If within each group the field variables are numbered 1 ≤ p ≤ Mj and
1 ≤ i ≤ Nj,p is the index of degrees of freedom belonging to the field
p, then the largest damped Newton error is estimated by
Here l is taken for all iterations in all substeps solving for the group
j,
αl,j is the damping factor,
ΔU l, j, k,p is the full Newton increment vector, and
Nj,p is the number of DOFs in the field
p. The weight factor
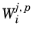
is described below.
is the relative increment over one complete iteration k. In this expression,
Uj,k,p is the segregated solution vector for the group
j.
where Sp is a scale factor that the solver determines from the settings in the
Scaling section of the
Field or
State node corresponding to
p under the
Dependent Variables node. There, the following choices are available in the
Method list:
For the Residual termination criterion, the segregated solver terminates after iteration k when the following convergence criterion is satisfied: For all the groups
j, the error estimate is smaller than the specified tolerance,
errj,k < tol, where
where F is the current residual, and
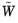
are the weights determined as explained under
Termination Criterion for the Fully Coupled and Segregated Attribute Nodes. The iterations can also terminate if the relative solution-based error is in the range of a hundred machine epsilon.
Pseudo time stepping is available in a stationary segregated approach as well; see Pseudo Time Stepping for a description of the CFL control. For the segregated solver, the error estimate
en in
Equation 20-1 is the arithmetic average of the errors in the different segregated groups.