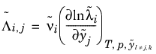In the Convection section, the mixture-averaged velocity of the electrolyte mixture is defined. The
Reference-electrode-stoichiometry based option defines the velocity based on the electrolyte current vector and the stoichiometry of the
Reference Electrode reaction. This option is applicable when computing steady-state current distributions when all charge-transfer reactions in the cell are the same as for the reference electrode. This option may also serve as a fair approximation in certain time-dependent problems. The
User defined option can be used to provide an arbitrary velocity expression, for instance velocity variables computed by a
Fluid Flow interface.
The Volumetric Equation of State section defines the interrelations between the total concentration of all species, the density, and the individual electrolyte component fractions. The equation of state may be based either on a
Density expression, or
Molar volumes. The density expression is typically composition dependent. Note that the species
Molar mass settings, defined on the interface top node, are also used when defining the state equations.
The Chemical Potentials section defines how composition changes impacts the chemical potentials of the electrolyte components. By default ideal conditions are assumed, implying that unit chemical activity coefficients are used. Enabling
Specify nonideal thermodynamic factors allows for defining all independent partial derivatives of the thermodynamic factors with respect to the electrolyte components.
equals the index of the component selected as Electrolyte component from molar-fraction constraint on the interface top node.