For the 1D, 2D, and 3D dimensions, geometry objects are created using the Geometric Primitives and importing CAD data from file. The
Geometry Operations can transform the objects, convert the object from one object type to another, and create a composite geometry object by forming unions, set differences, and set intersections of existing geometry objects. The object can be of the types solid, surface, curve, point, and mixed and are displayed beside the object name in
The Selection List Window, as shown in
Figure 7-1. It is also possible to check which objects are solid by adding a Clip Plane and select
Show Cross Section. It is also possible to set to highlight object overlaps with a red color, as shown in
Figure 7-1.
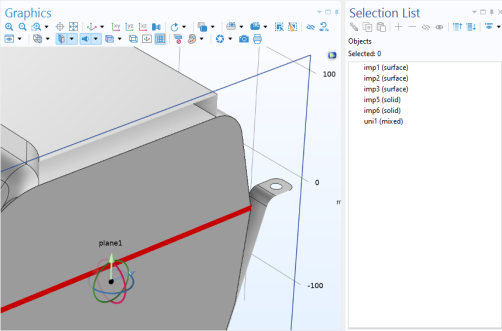
The created geometry objects are united or assembled and then analyzed and divided into a finalized geometry that consists of
geometric entities: domains, boundaries, edges, and points. The finalized geometry forms the basis for selecting geometric entities and then assigning and defining material properties, physics, and meshes. See
The Form Union/Assembly Node — Uniting the Geometry for information about forming a union or an assembly with the created geometry as its input. See also
Associative Geometry and Selections of Geometry Objects below.

