The Declarations node in the application tree is used to declare global variables and objects, which are used in addition to the global parameters and variables already defined in the model. Variables defined under the
Declarations node are used in form objects and methods. In form objects, they store values to be used by other form objects or methods. Variables that are not passed between form objects and methods, but that are internal to methods, do not need to be declared in the
Declarations node. In methods, variables defined under the
Declarations node have global scope and can be used directly with their name. For information on how to access global parameters defined in the model tree, see
Accessing a Global Parameter.
You can create a Declarations node that is local to a form. Such
Declarations for a form can only be used in that particular form, including form objects and methods that are local to the form.
Form Declarations can only be of the types:
Right-click a Declarations node to access the declaration types or use the ribbon.
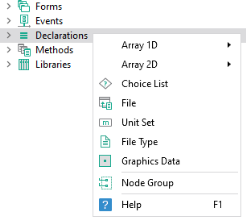
Note that Shortcuts are not created from this menu but by clicking the
Create Shortcut button next to the
Name in the
Settings window of a form object or by using Ctrl+K for a selected form object.
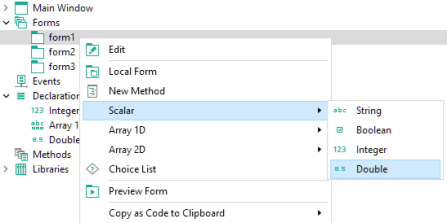
To create Declarations that are local to a form, right-click the corresponding form and select the variable type, as shown below.
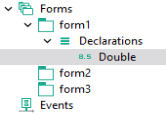
Variables that are local to a form are organized under a Declarations node that is a child node to the form, as shown below.
The first three types of declarations, Scalar,
Array 1D, and
Array 2D, can be of the following data types:
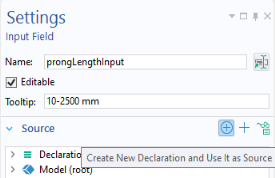
In addition to right-clicking the Declarations node, you can click the
Create New Declaration and Use It as Source button in the
Source section of many types of form objects.
The figure below shows a command sequence that includes a Plot Temperature command with an input argument
form1/graphics.
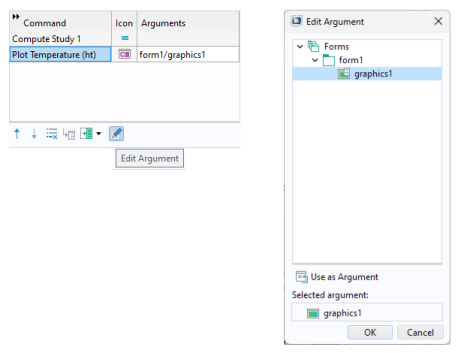
To use a scalar variable, 1D array, or 2D array as input arguments, you use the corresponding variable name. To access a single element of an array, or a row or column of a 2D array, use indexes. For example, to access the first component in a 1D array my_variable, you use
my_variable(1). A 2D array element can be retrieved as a scalar by using two indexes, for example,
my_matrix(2,3). The indexes can themselves be other declared variables, for example,
my_variable(n).
For commands requiring a graphics object as an input argument, only string type declarations are allowed with appropriate indexes, if necessary. If there is a graphics object named graphics1 and also a string declaration named
graphics1, then the contents of the string declaration will be used. An exception is if single quotes are used, such as
'graphics1', in which case the graphics object
graphics1 is used. This rule is also applied to other combinations of commands and input arguments.
The Name of a variable is a text string without spaces. The string can contain letters, numbers, and underscores. The reserved names
root and
parent are not allowed and Java
® programming language keywords cannot be used.




