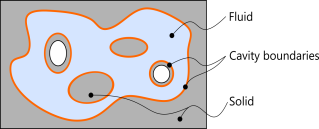
The enclosed volume is computed by defining a flux vector, which flows through all cavity surfaces. This flux is based on the position vector of the solid in its deformed and undeformed configuration. Using the divergence theorem the volume can be obtained from a surface integral.