You are viewing the documentation for an older COMSOL version. The latest version is
available here.
Add a Table Graph (
) plot to display data from a table with one line per output column. Right-click a
1D Plot Group,
Polar Plot Group, or
Smith Plot Group to add this plot type. First define a table to plot. This plot is also available from the plot groups’ contextual ribbon toolbars, by clicking
Graph Plot on the
Evaluation Group contextual ribbon toolbar (to plot the evaluation group in graph plot), or by selecting
Table Graph (
) from the
Table window’s toolbar. If desired, right-click the
Table Graph node to add a
Graph Marker,
Filter, or
Error Bars subnode.
Consider cases, with or without a Comparison subnode, where the COMSOL simulation and the reference values in the table graph have a different
x- or
y-axis range. Limiting the range of the table graph plot to coincide with the range of the COMSOL simulation plot can make it easier to interpret the plots. You can do so using two different methods:
|
•
|
Use the Preprocessing section (see below) in a Table Graph plot to scale and shift the values in the table, something that can be used to perform unit conversions. It is also possible to restrict the x- and y-axis ranges of the data.
|
|
•
|
Add a Filter subnode to perform more general filtering of the table data than what is supported by the Preprocessing section. You can for example, filter data in Column 1 to values between 0 and 100 using an expression like (co1>=0) && (col1<=100).
|
From the Source list, choose
Table or
Evaluation group, and then choose a table or evaluation group table with the data that you want to plot as a surface plot from the
Table of
Evaluation group list below. The list of tables includes Comparison tables, if
Comparison subnodes have been used under some 1D graph plots (see
Comparison).
From the x-axis data list (or
θ angle data for polar plots), select the column to use as
x-axis: Select
Row index to use the table’s row indexes (row numbers) as
x-axis, or leave it at
Automatic to let the software determine the input from the data in the table.
The Plot columns or
Plot rows (depending on if the
Row-based check box is selected or not) list controls which columns or rows to plot.
All excluding x-axis (or
All excluding θ angle list for polar plots) indicates all columns not used in
x-axis data (or
θ angle data). Select
Manual instead to specify which columns to plot in the
Columns or
Rows list.
If available, select a Transformation of the data from the table —
None (the default) to use the data directly without any transformation, or select
Discrete Fourier transform to use a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) to transform the data from a time-dependent solution to the frequency domain. If you select to display a DFT, choose one of the following options from the
Show list:
|
•
|
Real part, to show the real part of the output only.
|
|
•
|
Imaginary part, to show the imaginary part of the output only.
|
|
•
|
Amplitude, to show the amplitude of the output (the default).
|
|
•
|
Phase, to show the phase of the output.
|
|
•
|
Frequency spectrum, to display the function’s frequency spectrum by computing the number of frequencies and the frequency range based on the FFT (fast Fourier transform) of the function. The transform is valid for all functions, but what you get corresponds to a periodic continuation of the function outside the chosen bounds. To specify these values manually, select the Number of frequencies check box and enter a value in the associated field (the default is based on the number of time samples). From the Scale list, choose None (the default), Multiply by sampling point, or Divide by number of frequencies. You can choose to scale with the sampling period to show Fourier transform values instead of a pure DFT transform. Select the Scale check box to scale the values on the y-axis so that their magnitude reflects the magnitude of the original signal. The values then have the same unit as the input data for the FFT. For a pure sinusoid, the scaled value is the peak magnitude divided by the square root of 2 ( 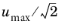 ). Select the Frequency range check box and then enter the bounds of the frequency range in the Minimum and Maximum fields (in Hz). The FFT algorithm uses resampling based on linear interpolation. The x-axis shows the frequency (in Hz). By default, the y-axis shows the unscaled Fourier coefficients.
|
If you have selected Amplitude or
Frequency spectrum, you can select the
In dB check box to present the values in dB. From the
dB type list, choose
10log (the default) or
20log. The display in dB requires a reference value. From the dB reference list, choose
Maximum (the default) to use the maximum value as the reference, or choose
Manual to enter a suitable reference value in the
Reference value field.
If you have selected Real part,
Imaginary part,
Amplitude, or
Phase, the following additional settings are available: To specify this value manually, select the
Number of uniform samples check box and enter a value in the associated field. If desired, select the
Inverse transform check box to use an inverse DFT. Select the
Mask DC check box to set the DC value (zero frequency component) to zero (not available if
Inverse transform is selected). The
Ignore last sample check box is selected by default to not include the last sample in the transform (not available if
Inverse transform is selected). The
Shift zero frequency and
Scale with sampling period check boxes are selected by default. Clear one or more of these check boxes if you want to exclude those steps.
If you have chosen None from the
Transformation list, use the
Sorting list to sort the data points with respect to
x- or
y-coordinates. Choose
None (the default, no sorting),
x-axis data, or
y-axis data.
By default, table plots only display the real data in a table, just as other plot types display real data unless you use the imag function in the expression. To display the imaginary part of complex-valued data in a table, when available, select the
Plot imaginary part check box. This option is only available when a transformation to the frequency domain is not used.
In the settings for a Smith Plot Group, this section includes a
Data interpretation list, where you can choose
Reflection (the default),
Impedance, or
Admittance.
Select the Plot on secondary y-axis check box to plot the
y-axis data on the secondary
y-axis to the right of the plot instead of the primary
y-axis to the left of the plot.
Under x-axis column and
y-axis column, you can use the following settings for preprocessing of the table data:
From the Transform list select:
|
•
|
None (the default), for no preprocessing of the data.
|
|
•
|
Linear, to preprocess the data using a linear transformation of the data values for the x- or y-axis column. You define the linear preprocessing with values for the scaling (default: 1) and the shift or offset (default: 0) in the Scaling and Shift fields, respectively. The default values do not change the original data values.
|
From the Range list select:
|
•
|
All (the default), to use the range for all data.
|
|
•
|
Manual, to specify range limits in the x minimum and x maximum fields, for the x-axis column, and the y minimum and y maximum fields, for the y-axis column. The default values for the minimum and maximum fields are −Inf and Inf, respectively.
|
Select the Show legends check box to display the plotted expressions to the right of the plot. In plots where each line represents a certain time value, eigenvalue, or parameter value, these values are also displayed.
When Automatic is selected from the
Legends list (the default), select or clear the
Label and
Headers check boxes to control what to include in the automatic legends (by default it includes the column headers only). You can add a prefix or a suffix to the automatic legend text in the
Prefix and
Suffix fields. If
Manual is selected from the
Legends list, enter your own legend text into the table.