Use a Linear Projection nonlocal coupling (
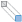
) when the argument is to be integrated along a line, and the line depends linearly on the evaluation point.
Select a Source frame from the list to evaluate the coordinates of the source vertices in the selected frame.
Then specify the linear projection by giving a set of points in the source and in the destination. The order of the vertices is significant. COMSOL Multiphysics constructs a linear projection from the source to the destination using the subspaces spanned by the vertices. Denote the map rank by n, denote the source vertices by
x0,
x1,...,
xn, and denote the destination vertices
x'0,
x'1,…,
x'n. After padding the source and destination vertices’ vectors with zeros as necessary, the software solves the following matrix equation for a
transformation matrix T and a
translation vector V:
Select an option from the Destination geometry list if there is more than one geometry in the model.
Enter an Integration order of the numerical integration method (default: 4). See
integration order in the
Glossary.