The Experiment node organizes the data and the conditions for a particular experiment. This is also where experimental variables are associated with model variables in order to set up the parameter estimation.
Right-click the Parameter Estimation node to add one or more
Experiment nodes. You can also select it from the
Reaction Engineering toolbar,
Attributes menu, enabled when the
Parameter Estimation node is selected.
Notice that the Experiment node requires the Optimization Module.
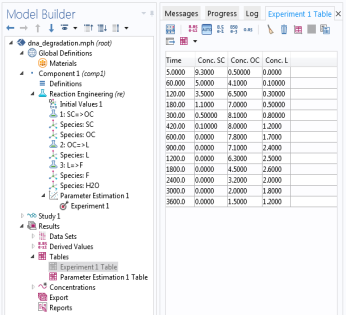
Experimental data is read into the software by importing comma-separated value files, CSV files. After import, identifiers display in the
Data column of the
Experimental Data table (
Figure 2-9). If the CSV files have column headers, these are used to identify the columns. If the data file does not have column headers, the columns are identified by a number. It is assumed that the first column corresponds to the independent variable for time (
t). In the
Model variables column, the measured data is correlated with model variables by entering the proper variable names or expressions. The
Use column controls whether to include data in the parameter estimation calculation or not. Data column entries require associated
Model variables to be accounted for the parameter estimation calculations.
In the Unit column, enter the unit of the imported experimental data.
In the Weight column, enter a strictly positive value. The difference between the value of the
Model variable and the
Data column value is squared and multiplied with the
Weight and a factor 0.5 to give the contribution to the total objective for each measured value.
Each Experiment node can be associated with user-defined parameters during the parameter estimation. For example, concentration transients can be measured for a number of different isothermal conditions.
Parameter name and
Parameter expression are added from a list. The list is populated with the parameters that are defined in the Parameters under Global Definitions in the Model Builder.
Initial conditions that change from one experiment to another need to be provided in the Initial States section. An entry in the
Parameter names column is added by choosing from a list of predefined variable names corresponding to the initial state of the reactor model.