The Wall node adds a selection of boundary conditions that describe the existence of a solid wall. The Wall node by default specifies no gas flux for the gas phase.
No slip is the default boundary condition for the liquid. A no slip wall is a wall where the liquid velocity relative to the wall velocity is zero. For stationary walls, it sets the liquid velocity to zero at the wall:
When Wall functions are selected, the
Apply wall roughness option becomes available. Click to select the
Apply wall roughness check box to apply the roughness correction. When the check box is selected, the default
Roughness model is
Sand roughness, which is derived from the experiments by Nikuradse. Select
Generic roughness to specify more general roughness types.
From the list, select a Gas boundary condition for the gas phase on the wall —
No gas flux (the default),
Gas concentration,
Gas outlet,
Gas flux, or
Symmetry.
For Gas concentration enter the
Effective gas density ρgϕg0 (SI unit: kg/m
3). The default is 0 kg/m
3.If
Solve for interfacial area is selected, also select either the
Bubble number density (the default) or the
Bubble diameter and gas density button.
For Gas flux enter the
Gas mass flux 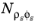
(SI unit: kg/(m
2·s)) (the default is 0 kg/(m
2·s)) and if the
Solve for interfacial area check box is selected on the physics interface, the
Number density flux Nn (SI unit: 1/(m
2·s)). The default is 0 (1/(m
2·s)).
The Translational velocity setting controls the translational velocity,
utr. The list is per default set to
Automatic from frame. When
Automatic from frame is selected, the physics automatically detects if the spatial frame moves. If there is no movement,
utr is set to
0. If the frame moves,
utr becomes equal to the frame movement.
utr is accounted for in the actual boundary condition prescribed in the
Liquid boundary condition section.
When Manual is selected from
Translational velocity selection list, the
Velocity of moving wall,
utr can be prescribed manually. Specifying the translational velocity manually does not automatically cause the associated wall to move. An additional Moving Mesh interface needs to be added to physically track the wall movement in the spatial reference frame.
The Sliding wall option is appropriate if the surface is sliding in its tangential direction. A velocity is prescribed at the wall and the boundary itself does not have to actually move relative to the reference frame.