Here, d is the shortest distance between the source center and the destination plane, and
rs is the radius of the source sphere.
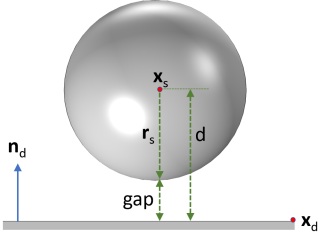
The shortest distance between the spherical source and the planar destination (d) is the projection of the distance between source center and a point located on the plane in the direction of the surface normal. It is calculated as
Here, Xsrc and
Xdst are the undeformed locations of the source center and a point on the destination plane, and
usrc and
udst are the corresponding displacements.
nd is the outward normal of the destination plane.
