The DES RBVMWV, Spalart-Allmaras (spf) interface (

) simulates turbulent single-phase flows by resolving the largest three-dimensional unsteady eddies and modeling the effect of the smaller eddies with the Residual Based Variational Multiscale method in the bulk and with the Spalart-Allmaras model near walls. The physics interface is currently only suitable for incompressible flows.
A different LES model can be selected under LES model. A RANS turbulence model can be selected by changing the
Turbulence model type to
RANS,
and a LES model can be selected by changing the
Turbulence model type to
LES. Laminar or creeping flow may be simulated by changing the
Turbulence model type to
None.
The DES RBVMWV, Spalart-Allmaras model employs per default an Automatic wall treatment, which switches between a low-Reynolds-number formulation and a wall-function formulation depending on how well resolved the flow is close to the wall. The automatic wall treatment gives a robust formulation that makes the most out of the available resolution.
Select the Low Re option in order to enforce resolution all the way down to the wall. This can be more accurate that the automatic wall treatment provided that the mesh is fine enough.
For this physics interface the parameters are Cμ, for the
Include synthetic turbulence option in the
Velocity inlet condition, the additional diffusion parameter
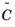
, and the Spalart-Allmaras parameters
Cb1,
Cb2,
Cv1,
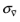
,
Cw2,
Cw3,
κv,
B and
CDES.
Select the Use dynamic subgrid time scale check box to use the time derivative from the previous time step to estimate temporal changes in the unresolved scales.