You are viewing the documentation for an older COMSOL version. The latest version is
available here.
To add a Reaction node (

) either right-click the
Chemistry node or on the
Chemistry toolbar click
Reaction.
Enter a chemical reaction Formula. Click
Apply to make the interface examine the species taking part in the model’s reactions and automatically add the associated
Species features to the Model Builder.
Select the Reaction type —
Reversible,
Irreversible, or
Equilibrium — or edit the expression directly in the
Formula field. In the latter case, specify the reaction type with a delimiter separating the two sides of the equation:
|
•
|
<=> denotes a Reversible reaction
|
|
•
|
=> denotes an Irreversible reaction
|
|
•
|
= denotes a reaction at chemical Equilibrium
|
Each Reaction type has its own set of reaction kinetics:
|
•
|
If the reaction is Reversible or Irreversible, the reaction rate for reaction i contributes to the change in species i as follows:
|
(2-98)
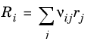
where νij is the stoichiometric coefficient.
|
•
|
If it is an Equilibrium reaction, the equilibrium expression is equal to the equilibrium constant:
|
This section is available when the Reaction type is either
Reversible or
Irreversible.
When Mass action law is selected (default), the rate expression is automatically derived from the stoichiometric coefficients in the reaction formula:
|
•
|
For an Irreversible reaction type, the reaction rate becomes:
|
(2-99)
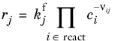
|
•
|
For a Reversible reaction type, the expression instead becomes:
|
(2-100)
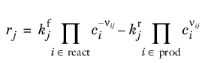
If the reaction order differs from the stoichiometric coefficients, or if an arbitrary rate expressions is applicable, change Reaction Rate to
User defined. An expression field
r appears with the default expression being that from the mass action law. Below this there are fields to set the reaction order. For a reversible reaction the reverse reaction order may be specified in addition to the forward one. The unit of the rate constant
k (or frequency factor
A in the case of Arrhenius behavior), is derived from the reaction order, in SI units: (m
3/mol)
α − 1/s, where
α equals the order with respect to volumetric species. When surface species are present — identified by their “(ads)” suffix — the unit is instead given by m
3α+2β − 2/mol
α+β−1/s, where
β is the order with respect to surface species.
This section applies for Reversible or
Irreversible reactions and defines the reaction rate constants used in the reaction rates.
The Forward rate constant kf is used for both
Reversible and
Irreversible reactions. The
Reverse rate constant kr is only used for
Reversible reactions (
Equation 2-99).
The Specify equilibrium constant check box is available for
Reversible reactions. If the check box is selected the rate constants are defined in a different manner with the reverse rate constant being computed from the following expression:
When the Use Arrhenius expressions check box is selected the Arrhenius parameters are automatically used in predefined expressions for the forward and reverse rate constants
kfand
kr, respectively.
Specify the activation energy and the frequency factor in the Arrhenius expressions to account for temperature variations. The reference temperature, Tref equals 1 K. The available fields are based on the
Reaction type chosen in the
Reaction node. Enter values or expressions for each of the following (reverse expressions are only available for reversible reactions):
This section is available for equilibrium reactions, and for reversible reactions when the
Specify equilibrium constant check box has been selected.
For an equilibrium reaction, specify the Equilibrium expression. When the
Equilibrium expression is set to
Automatic the following expression is used:
Select User defined from the
Equilibrium expression list to instead enter a manually defined equilibrium expression.
Specify the Equilibrium constant Keq0 for an equilibrium reaction, or for a reversible reaction when the
Specify equilibrium constant check box has been selected (in the
Rate Constants section).
The Equilibrium constant can either be
User defined, or automatically defined when set to
Automatic or
Thermodynamics.
Use the Automatic option to compute the equilibrium constant for an ideal system.
The Thermodynamics option is available when all reactions in the interface are equilibrium reactions, and the interface is fully coupled to a
Thermodynamic System (see
Species Matching). Use this setting to automatically compute the equilibrium constant for an ideal or nonideal system, dependent on the thermodynamic model applied for the coupled system.
Using Automatic or
Thermodynamics,
Keq0 is calculated from the Gibbs free energy of the reaction. For more details see
The Equilibrium Constant and the
Automatically Defined Equilibrium Constants section therein.
The Enthalpy of reaction H (SI unit: J/mol) is calculated by the interface from species properties and the related stoichiometric coefficients:
(2-101)
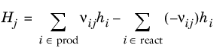
The Entropy of reaction S (SI unit: J/(mol·K)) comes from a similar expression:
(2-102)
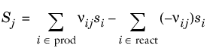
In Equation 2-101 and
Equation 2-102,
hi and
si are the species’ molar enthalpy and molar entropy, respectively.
Enter these quantities in the Species Thermodynamic Expressions section for the
Species node either by using the predefined polynomial or by providing a custom expression or constants.
The stoichiometric coefficients, νij, are defined as being negative for reactants and positive for products. Using
Equation 2-101 and
Equation 2-102 to equate the Gibbs free energy of reaction enables the equilibrium constant to be expressed according to
Equation 2-101.
The Heat source of reaction (SI unit: W/m
3) is automatically computed from the heat of each reaction
j, given by: