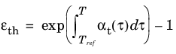Use the Thermal Expansion subnode to add an internal thermal strain caused by changes in temperature.
The Thermal Expansion subnode is only available with some COMSOL products (see
https://www.comsol.com/products/specifications/).
The Volume reference temperature Tref is the temperature at which there are no thermal strains. As a default, the value is obtained from a
Common model input. You can also select
User defined to enter a value or expression for the temperature locally.
The Temperature T is by default obtained from a
Common model input. You can also select an existing temperature variable from a heat transfer interface (for example,
Temperature (ht/sol1)), if any temperature variables exist. or manually enter a value or expression by selecting
User defined.
Select an Input type to select how the thermal strain is specified. The default is
Secant coefficient of thermal expansion, in which case the thermal strain is given by
where α is the secant coefficient of thermal expansion.
α can be temperature dependent.
When Input type is
Tangent coefficient of thermal expansion, the thermal strain is given by
where αt is the tangential coefficient of thermal expansion.
When Input type is
Thermal strain, enter the thermal strain
dL as function of temperature explicitly.
In all three cases, the default is to take values From material. When entering data as
User defined, select
Isotropic,
Diagonal, or
Symmetric to enter one or more components for a general coefficient of the thermal expansion tensor or the thermal strain tensor. When a nonisotropic input is used, the axis orientations are given by the coordinate system selection in the parent node.
Physics tab with Linear Elastic Material,
Hyperelastic Material,
Nonlinear Elastic Material,
Elastoplastic Soil Material,
Piezoelectric Material, or
Magnetostrictive Material node selected in the model tree: