
|
|
•
|
In supersaturation conditions, i.e. cv>csat, there is condensation on the surfaces, and the flux is negative (outgoing flux on the boundaries of the computational domain), equal to MvK(csat-cv). The liquid concentration on the surface increases.
|
|
•
|
In subsaturation conditions, i.e. cv<csat, and when there is some liquid on the surface, there is evaporation from the surfaces, and the flux is positive (ingoing flux on the boundaries of the computational domain), equal to MvK(csat-cv). The liquid concentration on the surface decreases.
|
|
•
|
In subsaturation conditions, i.e. cv<csat, and when there no liquid on the surface, the flux is null.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Browse to the model’s Application Libraries folder and double-click the file condensation_electronic_device.mph.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Find the Physics interfaces in study subsection. In the table, clear the Solve check box for Study 1.
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1)>Moisture Transport in Air (mt) click Initial Values 1.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, expand the Component 1 (comp1)>Heat Transfer in Solids and Fluids (ht) node, then click Moist Air 1.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, expand the Component 1 (comp1)>Definitions node, then click Domain Probe 1 (dom1).
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Click
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click Replace.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, expand the Maximum Relative Humidity node, then click Probe Table Graph 1.
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
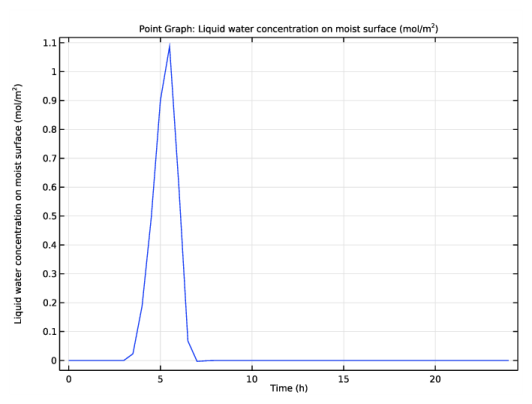
In the Settings window for 1D Plot Group, type Liquid water concentration over time in the Label text field.
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|