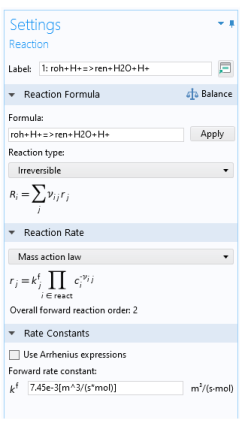
In each Reaction node, specify the reaction
Formula and
Reaction type of a single chemical reaction.
Right-click any Reaction node to disable and enable the corresponding node in the
Model Builder. Creating reaction subsets in this way is a straightforward approach to investigate the influence of individual reactions on the overall reaction system. Species that take part only in deactivated reactions are automatically deactivated, as indicated by the unavailable
Species feature nodes. If a reaction is deleted, the interface automatically deletes those species that take part only in the deleted reactions.
When chemical formulas are entered, each reaction is associated with a unique ID (identification) number (Figure 2-2). The ID number is not a row number but rather an absolute reference number to a given reaction. This means that a reaction keeps its ID number, even if reactions are deleted with a lower number. Furthermore, constants and expressions within fields associated with a given reaction are also indexed with the reaction number.
The Name prepended to the variable name is called the variable scope. Defaults are
re and
chem for the Reaction Engineering and Chemistry interface, respectively. All variables set up by the interface are given the same scope. The variable scope can be useful to couple the equations of different physics interfaces.
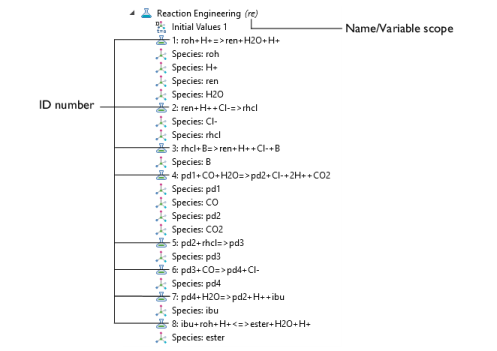
As a general labeling rule, the variable name that refers to the contents of a field associated with a Reaction node is given by the physics interface
Name, followed by the field name, and ends with the reaction ID number. For example, the contents of the reaction rate field
r for Reaction 1 is assigned the variable name
re.r_1.