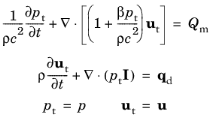The Nonlinear Pressure Acoustics, Time Explicit Model node adds the equations for modeling the propagation of nonlinear acoustic waves. The nonlinear continuity equation and momentum equation solved are given by:
where pt is the total acoustic pressure and
ut is the total acoustic velocity fluctuations. Because the problem solved is nonlinear the superposition principle does not apply which means that the “total” fields are always equal to the dependent variables.
In the Settings window, define the properties for the acoustics model, model inputs, and material properties.
Select the Fluid model —
Linear elastic,
Viscous,
Thermally conducting,
Thermally conducting and viscous,
General dissipation, or
Ideal gas. The settings are the same as for the
Pressure Acoustics, Time Explicit Model.
Select how to define the Coefficient of nonlinearity β —
From parameter of nonlinearity (default) or
User defined. The
Parameter of nonlinearity B/A can be taken
From material or entered as a
User defined expression. For the
Ideal gas fluid model, it is also possible to compute the
Coefficient of nonlinearity β From ratio of specific heats.
To display this section, click the Show More Options button (

) and select
Advanced Physics Options in the
Show More Options dialog box. By default, the filter parameters
α,
ηc, and
s are not active. Select the
Activate check box to activate the filter. The filter provides higher-order smoothing for the DG formulation. Inside absorbing layers the settings given here are overridden by the
Filter Parameters for Absorbing Layers.