|
This section is only available when the Allow multiple release times property is active. This can be found in the Advanced section of the physics interface settings when Advanced Physics Options are shown in the Model Builder.
|
|
The Density proportional to expression must be strictly positive.
|
|
•
|
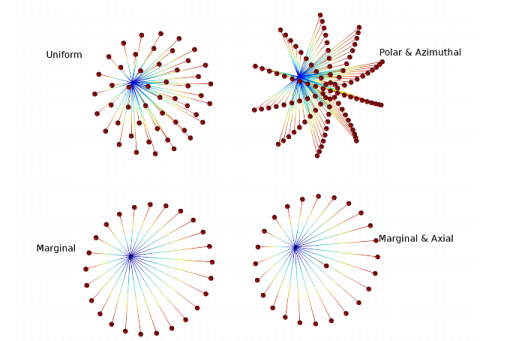
For Expression a single ray is released in the specified direction. Enter coordinates for the Ray direction vector L0 (dimensionless) based on space dimension.
|
|
•
|
For Spherical a number of rays are released at each point, sampled from a spherical distribution in wave vector space. Enter the Number of rays in wave vector space Nw (dimensionless). The default is 50.
|
|
•
|
For Hemispherical a number of rays are released at each point, sampled from a hemispherical distribution in wave vector space. Enter the Number of rays in wave vector space Nw (dimensionless). The default is 50. Then enter coordinates for the Hemisphere axis r based on space dimension.
|
|
•
|
For Conical a number of rays are released at each point, sampled from a conical distribution in wave vector space. Enter the Number of rays in wave vector space Nw (dimensionless). The default is 50. Then enter coordinates for the Cone axis r based on space dimension. Then enter the Cone angle α (SI unit: rad). The default is π/3 radians.
|
|
•
|
The Lambertian option is only available in 3D. Anumber of rays are released at each point, sampled from a hemisphere in wave vector space with probability density based on the cosine law. Enter the Number of rays in wave vector space Nw (dimensionless). The default is 50. Then enter coordinates for the Hemisphere axis r based on space dimension.
|
|
•
|
For Specify polar and azimuthal distributions specify the Number of polar angles Nφ (dimensionless) and the Number of azimuthal angles Nθ (dimensionless). Rays are released at uniformly distributed polar angles from 0 to the specified cone angle. A single axial ray (φ = 0) is also released. For each value of the polar angle, rays are released at uniformly distributed azimuthal angles from 0 to 2π. Unlike other options for specifying the conical distribution, it is not necessary to directly specify the Number of rays in wave vector space Nw (dimensionless), which is instead derived from the relation
|
|
•
|
For Marginal rays only the rays are all released at an angle α with respect to the cone axis. The rays are released at uniformly distributed azimuthal angles from 0 to 2π.
|
|
•
|
For Marginal and axial rays only the rays are all released at an angle α with respect to the cone axis, except for one ray which is released along the cone axis. The marginal rays are released at uniformly distributed azimuthal angles from 0 to 2π.
 |
|
•
|
the Intensity computation is set to Compute intensity, Compute intensity and power, Compute intensity in graded media, or Compute intensity and power in graded media in the physics interface Intensity Computation section, and
|
|
•
|
Expression is selected as the Ray direction vector.
|
|
•
|
the Intensity computation is set to Compute intensity, Compute intensity and power, Compute intensity in graded media, or Compute intensity and power in graded media in the physics interface Intensity Computation section, and
|
|
•
|
Expression is selected as the Ray direction vector.
|
|
•
|
For an idealized plane wave the radii of curvature would be infinite. However, because the algorithm used to compute intensity requires finite values, when Plane wave is selected the initial radii of curvature are instead given an initial value that is 108 times greater than the characteristic size of the geometry.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
For an Ellipsoid, enter the Initial radius of curvature, 1 r1,0 (SI unit: m) and the Initial radius of curvature, 2 r2,0 (SI unit: m). Also enter the Initial principal curvature direction, 1 e1,0 (dimensionless).
|
|
•
|
For Fully polarized and Partially polarized rays in 3D enter an Initial polarization parallel to reference direction a1,0 (dimensionless), Initial polarization perpendicular to reference direction a2,0 (dimensionless), and Initial phase difference δ0 (SI unit: rad).
|
|
•
|
For Fully polarized and Partially polarized rays in 2D enter an Initial polarization, in plane axy,1 (dimensionless), Initial polarization, out of plane az,0 (dimensionless), and Initial phase difference δ0 (SI unit: rad).
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
when the Intensity computation is set to Compute intensity or Compute intensity in graded media under the physics interface Intensity Computation section, and
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
It is also available when the Intensity computation is Compute intensity and power or Compute intensity and power in graded media under the physics interface Intensity Computation section, and any choice of Ray direction vector displays this section.
|
|
The relationship between the photometric horizontal, photometric vertical, and ray direction vector, and its effect on the initial ray intensity, is explained in ANSI/IESNA LM-63-02 (R2008), IESNA Standard file format for the electronic transfer of photometric data and related information, Illuminating Engineering Society (2002).
|
|
Currently the Photometric Data Import feature does not support the options TILT=INCLUDE or TILT=<FILENAME> that are included in some IES files. Only TILT=NONE is allowed.
|