Use a Global Matrix Evaluation (
) to define the evaluation of the numerical values for a global matrix variable such as S-parameters in a model with several ports activated as a parametric sweep and a frequency-domain study. The
Table window then displays all values for all frequencies in a parametric sweep.
The Ignore NaN check box is selected by default to ignore NaNs in the data for an inner or outer data series operations. If you want to keep values that are NaN, clear this check box. This setting is useful when solving a parametric sweep that computes a single column of the matrix variable at each step, such as when running a Port or Terminal sweep in the AC/DC Module or the RF Module. If the
Ignore NaN check box is selected, the columns not computed in each step (that are filled with NaN) are ignored when evaluating the complete matrix.
This section allows specifying a transformation to be applied on the evaluated matrix. The result of the transformation is displayed in the Table window. Select a
Transformation for the matrix. If
None is selected, the evaluated matrix is displayed. If
Inverse is selected, the inverse of the evaluated matrix is displayed.
The additional transformations available in the list (such as From S to Z) can be used in electrical applications to transform between different lumped parameter matrices of the system, such as the system’s impedance matrix,
Z; admittance matrix,
Y; and S-parameter matrix,
S. These matrices are computed in Port or Terminal sweeps (using the AC/DC Module or the RF Module), and are related by simple transformations,
where Z0 is the characteristic impedance and
Y0 the characteristic admittance of the ports or terminals. In general, only one of the three matrices is computed by the physics interface and becomes available for evaluation.
You can also make a transformation from Maxwell capacitance to mutual capacitance or vice versa by selecting From Maxwell to mutual or
From mutual to Maxwell, and from an inverse Maxwell capacitance to mutual capacitance by selecting
From inverse Maxwell to mutual (the inverse Maxwell capacitance is the output from sweeps over lumped parameters in electromagnetics). The relationship between the Maxwell capacitance matrix
MA and the mutual capacitance matrix
MU is that
MUij is equal to
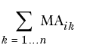
if
i = j, or equal to
−MAij otherwise.