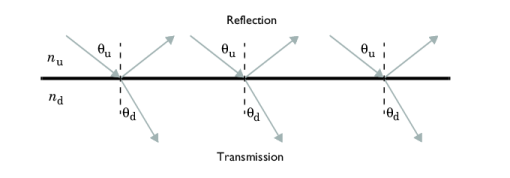
Here, nu and
nd are the refractive indices of the adjacent domains. The angle of incidence
θu and the angle of transmission
θd are measured with respect to the surface normal so they correspond to the polar angles with the refractive surface.
Once the directional function of surface properties are calculated, there remains an issue to handle. When nu > nd, the angle of transmission
θd is greater than the angle of incidence
θu. This leads to the appearance of a critical angle
θc above which
θd cannot be calculated because the arcsine is only defined in the interval [
−1, 1]. The critical angle is
Which is the value of θu that leads to
θd equal to
π/2. Above this critical angle, all the incident radiation is reflected and nothing is transmitted. When
nu > nd, the arcsine is well defined for the whole range of
θu.