The Label is the default physics interface name.
The Name is used primarily as a scope prefix for variables defined by the physics interface. Refer to such physics interface variables in expressions using the pattern
<name>.<variable_name>. In order to distinguish between variables belonging to different physics interfaces, the
name string must be unique. Only letters, numbers, and underscores (_) are permitted in the
Name field. The first character must be a letter.
The default Name (for the first physics interface in the model) is
mt.
In 2D and 1D axisymmetric components, set the Thickness dz, which is the thickness of the domain in the out-of-plane direction. The default value is 1 m.
In 1D components, set the Cross-sectional area Ac and the
Cross-sectional perimeter Pc of the domain. Default values are 1 m
2 and
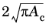
, respectively.
Set the Reference vapor concentration, which is used when the moisture transport interface is coupled to a fluid flow interface with the
Incompressible flow option selected in the
Compressibility list. In this case, the fluid density is evaluated at the
Reference pressure level (defined in the
Physical Model section of the fluid flow interface), at the temperature defined in the domain features of the moisture transport interface (293.15 K), and at the
Reference vapor concentration specified in this section.
The Streamline diffusion checkbox is selected by default and should remain selected for optimal performance for applications that include a convective or translational term.
Crosswind diffusion provides extra diffusion in regions with sharp gradients. The added diffusion is orthogonal to the streamlines, so streamline diffusion and crosswind diffusion can be used simultaneously. The
Crosswind diffusion checkbox is also selected by default and is only available when the
Streamline diffusion checkbox is selected.
The Isotropic diffusion option (not selected by default) adds an additional term to the diffusion coefficient to dampen spurious oscillations caused by convective terms. Increasing the
Tuning parameter δid amplifies the effect of the isotropic diffusion. As a rule of thumb, the tuning parameter should be large enough to ensure convergence, while remaining as small as possible as it reduces the accuracy of the original problem.
To display this section, click the Show More Options button (

) and select
Advanced Physics Options. These settings only apply to the domains in which a
Moist Air feature is active. Select a
Convective term —
Nonconservative form (the default) or
Conservative form. The latter should be used for compressible flow.
Note that Diluted Species and
Concentrated Species formulations are equivalent when using
Conservative form, they can both be used for large vapor concentrations.
To display all settings available in this section, click the Show More Options button (

) and select
Advanced Physics Options in the
Show More Options dialog. The shape functions used for the relative humidity are by default
Quadratic Lagrange in building materials, and
Linear in moist air and porous media. Note that when a porous medium is used with
Equilibrium between liquid and gas phases set to
Nonequilibrium formulation, an additional dependent variable is solved for, the liquid saturation, which uses the same type of shape functions as the relative humidity.