For the sake of brevity, consider the 1D Equation 2-62. In order to derive the PML formulation in the time domain, the following steps are taken (
Ref. 40). First, consider a special form of the mapping
Equation 2-61:
Then, taking Equation 2-63 into account, multiply
Equation 2-62 by
1 + σ(x)/iω.
Equation 2-62 transforms to the following form:
The transformation to the time domain is performed according to the rule iωp → ∂p/∂t. Its direct application to
Equation 2-64 would result in a time integral of
p. To avoid this, an auxiliary variable
u is introduced:
Equation 2-64 and
Equation 2-65 yield a system of partial differential equations in the time domain equivalent to the frequency domain
Equation 2-62:
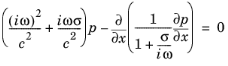 .
.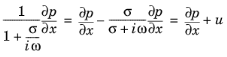 .
.