Use an Import (

) node to import geometry objects from a file or from another geometry, as shown in
Figure 7-49.
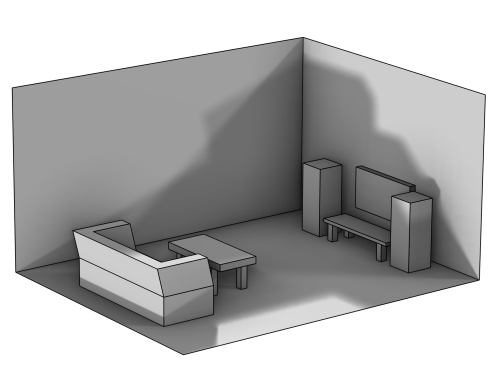
To add an Import operation, click
Import (

) in the
Geometry toolbar. You can also right-click the
Geometry node to add this node from the context menu. Then enter the properties of the import feature in the
Import section of the
Settings window for the
Import node.
In the Source list choose the type of data to import:
Any importable file and
COMSOL Multiphysics file are always available. If there is another geometry sequence of the same dimension in the model, the type
Geometry sequence is available. In addition, you can choose
Mesh in 1D;
DXF file and
Mesh in 2D; and
Mesh or 3D printing file (STL, 3MF, PLY) in 3D.
|
|
If you have license for the CAD Import Module, you also have 3D CAD file in 3D (see the CAD Import Module User’s Guide for more information about supported CAD file formats). You need to use the CAD kernel for the geometry representation, which you can specify in the Preferences window and in the Settings window for Geometry.
|
In all cases, you need to specify the geometry sequence, mesh, or file to import. Then click Import to bring in the geometry or mesh to use as a part of the geometry in the geometry sequence.
For the Any importable file and
COMSOL Multiphysics file source types (and the 3D CAD, 2D DXF, and 2D and 3D ECAD file source types), specify the filename in the
Filename field or click the
Browse button (

). You can also click the downward arrow beside the
Browse button and choose
Browse From (
) to open the fullscreen
Select File window. Click the downward arrow for the
Location menu (

) to choose
Show in Auxiliary Data (
) to move to the row for this file in the
Auxiliary Data window,
Copy Location (

), and (if you have copied a file location)
Paste Location (

).
For DXF, mesh and 3D printing file formats, and 3D CAD import, you can change a number of properties when you have selected the file type from the Source list. To import the file, click the
Import button (

). If you have changed some property, the software automatically reimports the file when you click a build button. If you have changed the source file, you need to explicitly click the
Import button to read the modified file.
In 2D and 3D, when COMSOL Multiphysics file is selected from the
Source list, the
Include result from virtual operations checkbox is selected by default. Clear that checkbox if you want to exclude the virtual operations in the file when importing it into another geometry.
In 2D, when DXF file is selected from the
Source list, in the
Layer selection list, select the layers to import.
In 2D, when DXF file is selected from the
Source list, under
Knitting of curves, select
Form solids to unite all objects in each layer and make all void regions solid, select
Knit curves to unite all objects in each layer, or select
Do not knit to do nothing.
The repair tolerance specifies the largest distance between the endpoints of curves allowed in the imported geometry. You can specify this tolerance as an import option. If the Repair imported objects checkbox is selected, in the
Repair tolerance list choose between
Automatic (default) and
Relative. For the option
Relative, enter a
Relative repair tolerance (default 1e-5). To create a geometry for mesh generation and finite element analysis, COMSOL Multiphysics requires a high degree of accuracy within the CAD drawing. Sometimes DXF geometries contain small gaps and exceedingly short edges that make it impossible to create a valid 2D solid or a valid mesh. COMSOL Multiphysics provides repair tolerance settings to remove short edges and close small gaps during DXF file import. The absolute repair tolerance is the relative repair tolerance times the maximum coordinate of the imported objects (the default value is 10
−5). Geometric entities that have a distance less than the absolute repair tolerance are merged.
Select the Resulting objects selection checkbox to create predefined selections (for all levels — objects, domains, boundaries, edges, and points — that are applicable) in subsequent nodes in the geometry sequence. To also make all or one of the types of resulting entities (domains, boundaries, edges, and points) that the objects consist of available as selections in all applicable selection lists (in physics and materials settings, for example), choose an option from the
Show in physics (
Show in instances if in a geometry part;
Show in 3D in a plane geometry under a work plane in a 3D component) list:
All levels,
Domain selection,
Boundary selection,
Edge selection, or
Point selection. The default is
Domain selection, which is suitable for use with materials and physics defined in domains. For use with a boundary condition, for example, choose
Boundary selection. These selections do not appear as separate selection nodes in the model tree. Select
Off to not make any selection available outside of the geometry sequence. From the
Color list, choose a color for highlighting the resulting objects selection. See
Selection Colors.
Select the Individual objects selections checkbox to create predefined selections (for all levels — objects, domains, boundaries, edges, and points — that are applicable) in subsequent nodes in the geometry sequence for each individual object in the geometry file and for each relevant entity level. To also make all or one of the types of resulting entities (domains, boundaries, edges, and points) that the objects consist of available as selections in all applicable selection lists (in physics and materials settings, for example), choose an option from the
Show in physics (
Show in instances if in a geometry part) list:
All levels,
Domain selection,
Boundary selection,
Edge selection, or
Point selection. The default is
Domain selection, if available, which is suitable for use with materials and physics defined in domains. For use with a boundary condition, for example, choose
Boundary selection. These selections do not appear as separate selection nodes in the model tree. Select
Off to not make any selection available outside of the geometry sequence.
Select the Construction geometry checkbox to make the resulting objects available only in the feature’s geometry sequence. For more information, see
Construction Geometry.
|
|
|
•
|
For a 3D example, Eigenmodes of a Room: Application Library path COMSOL_Multiphysics/Acoustics/eigenmodes_of_room.
|
|
•
|
For a 2D example, see Pore-Scale Flow: Application Library path Subsurface_Flow_Module/Fluid_Flow/pore_scale_flow.
|
|

