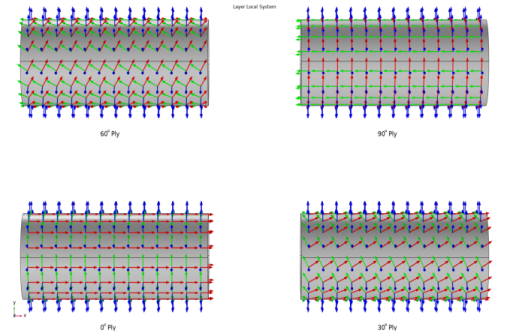
The stacking sequence of a composite laminate is [0/30/60/90]. The first axis of the laminate coordinate system is aligned with the global
x direction. This can be created by setting the
Create first tangent direction from option to
Global Cartesian (spatial), and by setting the
Axis to
x.
The stacking sequence of a composite laminate is [-15/15/-45/45]. The first axis of the laminate coordinate system is at
45° to the global
x direction. This can be created by defining a
Cylindrical System having
Longitudinal axis as
x-axis. Then set the
Create first tangent direction from to
Cylindrical System and the
Axis to
Manual with
{0,-1,1} as the orientation.
The stacking sequence of a composite laminate is [0/30/60/90]. The first axis of laminate coordinate system is aligned with the global
x direction but with the normal direction pointing inward. This coordinate system can be created in a same way as in the first example. In addition to that, the
Reverse Normal direction option is selected in the
Boundary System node in order to flip the normal vector.