here, T0 is the (constant) temperature of the gas,
Mn is the molar mass, and
R is the universal gas constant. The total gas pressure,
pA = pref + pfilm, is written in terms of the reference pressure level
pref and the pressure developed in the thin-film flow,
pfilm. Substituting this density into
Equation 9-3 and dividing it by
Mn/RT0 results in the modified Reynolds equation for ideal (isothermal) gases:
When the Compute implicit height change from wall velocity checkbox and/or
Compute implicit height change from base velocity checkbox are selected, the height changes due to the wall and/or base velocity are computed as,
For a gas, the slip length is often expressed using the mean free path,
λ, and a
tangential momentum accommodation coefficient,
α. The following definition of the mean free path is used in the Thin-Film Flow interfaces:
where μ is the gas viscosity,
p is the gas pressure,
R is the molar gas constant,
T is the temperature, and
Mn is the molar mass of the gas. This definition differs from the equivalent free path in
Ref. 3 by a factor
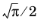
.
Values for the a tangential momentum accommodation coefficient,
α for various gas- surface combinations are given in
Ref. 2.