When solving for the scattered field in 2D axisymmetry, the background wave type can be set to a linearly polarized plane wave propagating in arbitrary direction in the Settings of
The Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain Interface. The linearly polarized plane wave is of the form
Eb = E0ej(ωt − (k ⋅ r)). In Cartesian coordinates,
E0 = (Ex,
Ey,
Ez),
k = (kx,
ky,
kz), and
r = (x,
y,
z). To express a linearly polarized plane wave with arbitrary incident angle and polarization angle in cylindrical coordinates for a 2D axisymmetric simulation, use the following expansions:
where θ is the angle with respect to the positive
z-axis,
ϕ is the azimuthal angle,
m is the azimuthal mode number, and
Jm is the Bessel function of the first kind of order
m. Furthermore, the basis vectors
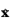
and
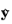
in Cartesian coordinates can be expressed with basis vectors
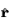
and
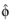
as
Here, θ and
α are defined as the schematic shown in
Figure 3-2. Once the linearly polarized plane wave is used as the background field, an auxiliary sweep over the azimuthal mode number will be added. After the simulation, the total scattered field is given by the sum of all the azimuthal modes. The
z-components of the scattered field and the background field will be plotted by default. Other components of the field can be computed in a similar way with the help of the
sum and
withsol operators.
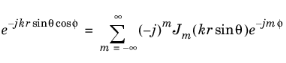 ,
,