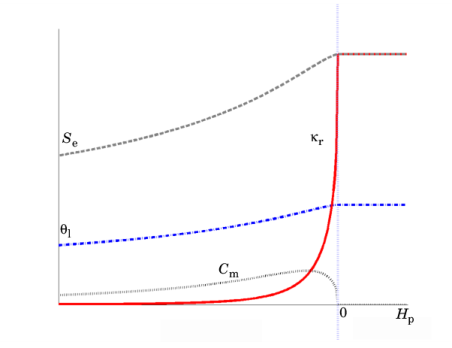
where the pressure, p, is the dependent variable. In this equation,
Cm represents the specific moisture capacity,
Se denotes the effective saturation,
Sp is the storage coefficient,
κs gives the hydraulic permeability at saturation,
μ is the fluid dynamic viscosity,
κr denotes the relative permeability,
ρ is the fluid density,
g is acceleration of gravity,
D represents the elevation, and
Qm is the fluid source (positive) or sink (negative).
where u is the velocity vector. The porous medium consists of pore space, fluids, and solids, but only the liquids move. The equation above describes the flux as distributed across a representative surface. To characterize the fluid velocity in the pores, COMSOL Multiphysics also divides
u by the liquid volume fraction,
θl. This interstitial, pore or average linear velocity is
ua = u/θl.