Many of the material models in COMSOL Multiphysics will compute a stress based on an elastic strain. The elastic strain tensor is obtained after removing any inelastic deformation contribution from the total deformation from the displacements.
In the finite deformation case, the inelastic strain is instead removed using a multiplicative decomposition of the deformation gradient tensor. The elastic deformation gradient tensor is the basis for all strain energy formulations in hyperelastic materials, and also for the elastic strain in linear and nonlinear elasticity. It is derived by removing the inelastic deformation from the total deformation gradient tensor. See
Multiplicative Decomposition in the
Structural Mechanics Theory chapter.
The External Strain subnode allows you to provide inelastic strain contributions to the
Hyperelastic Material, Layered.
Select a Coordinate system. All inputs that you give below are interpreted in the given coordinate system. Deformation gradients are rotated by the local system in both indices.
For Deformation gradient, enter an inelastic deformation gradient contribution
Fext. From the
External deformation gradient list, you can choose
User defined, or any deformation gradient tensor which is announced by another physics interface. If you select
User defined, enter values or expressions for the components of the deformation gradient tensor.
For Deformation gradient, inverse, enter an inelastic inverse deformation gradient contribution
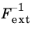
. From the
External deformation gradient inverse list, you can choose
User defined, or any inverse deformation gradient tensor which is announced by another physics interface. If you select
User defined, enter values or expressions for the components of the inverse deformation gradient tensor.
For Stretches, enter values or expressions for the three principal stretches. Entering data on this form is convenient for some simple geometries and strain states, but in general it is difficult to provide suitable a coordinate system for the principal orientations.
Physics tab with Hyperelastic Material, Layered node selected in the model tree: