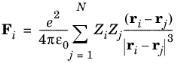where r is the distance between the particles (SI unit: m),
ε is the interaction strength (SI unit: Nm), and
σ is the collision diameter (SI unit: m).
A typical interaction strength is around 1.6·
10−21 J and a typical collision diameter is around
3.3·
10−10 m (
3.3 Å). The first term in the square brackets is a repulsive force due to internuclear repulsion, and the second term is an attractive force known as the
London dispersion force (LDF). The variation of the force with distance is plotted in
Figure 3-8.
where ks is the spring constant (SI unit: N/m) and
r0 is the equilibrium distance between particles (SI unit: m).