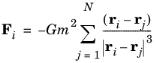Use the Particle-Particle Interaction node to make particles exert forces on each other. There are predefined options available for the Coulomb, Lennard-Jones, and linear elastic forces. It is also possible to define arbitrary expressions for the interaction force.
Select an option from the Interaction force list:
Coulomb (the default),
Linear elastic,
Lennard-Jones, or
User defined. If the default,
Coulomb, is kept, a Coulomb force describes the interaction between charged particles. No user input is necessary.
For Linear elastic enter the
Spring constant ks (SI unit: N/m). The default is
1 N/m. Enter the
Equilibrium distance between particles r0 (SI unit: m). The default is
1 mm.
For Lennard-Jones it uses the Lennard–Jones potential to approximate the interaction between neutral particles. The value of these parameters depend on the gas molecules interacting and can usually be found from a literature search.
For User defined enter a user-defined expression for the interaction
Force Fu (SI unit: N) based on space dimension.
The particle degrees of freedom are given the variable names qx,
qy, and
qz (in 3D), but to access the position vector of neighboring particles use the expression
dest(qx),
dest(qy), and
dest(qz).
As an example, the gravitational force on particle i depends on the position vector and mass of all other particles:
where ri is the position vector of the
ith particle,
G is the gravitational constant, and
m is the mass. To enter this as a user-defined force, enter (in 2D):
where tol is a user-defined parameter to prevent divide by zero for the
ith particle. In practice it is quite difficult to choose the value of
tol. It should in general be a small fraction of the smallest distance you want to allow between particles.
When reading or writing the expressions for a user-defined particle-particle interaction force, the dest() operator is used to identify properties of the particle that is being subjected to a force, while the omission of the
dest() operator indicates some property of a particle that is exerting the force. For example, when computing the force on the
ith particle, the expression
qx-dest(qx) is the difference between the
x-coordinate of some other particle (say, the
jth particle) and the
x-coordinate of the
ith particle.
By default, the Exclude Jacobian contribution for particle-particle interaction force check box is selected. This means the contribution to the Jacobian matrix is ignored due to the particle-particle interaction force. This also means that the problem solves much faster and requires much less memory. The drawback of this is that the Jacobian is not exact, and the solver therefore needs to take very small time steps when solving.
By default, the Apply cutoff length check box is cleared. If this check box is selected, enter a value or expression for the
Cutoff length rc (SI unit: m). The default is 5 mm. If the distance between particles is greater than the cutoff length, the particle-particle interaction force between them is set to zero.