Uses a Least-Squares Objective feature to create an objective function representing the sum of squared differences between measurements,
Pi, stored in an experimental data file and a corresponding expression,
P(u(ξi),
ξi), evaluated in the COMSOL Multiphysics model.
where ξi are the parameters to be estimated. The model expression is evaluated using interpolation on the feature’s selection, at measurement locations specified in the data file.
To create a least-squares objective, first import an Experimental Data file containing comma-separated or semicolon-separated columns of measurement data from a single experiment. Each
Least-Squares Objective feature corresponds to an experiment where the measurements have been obtained using given values for a set of
Experimental Parameters (for example, the temperature during the experiment). The squared sum of the difference between the measurement values and the corresponding expressions evaluated in the model — when solved for the given parameter values — is added as a contribution to the total least-squares objective function.
Right-click the node to add column subnodes — Value Column,
Time Column,
Parameter Column,
Coordinate Column, and
Ignored Column — assigning meaning to the individual columns as values, times, parameter values, coordinate data, or values to ignore, respectively. One column subnode must be added for each column in the data file and in the same order as the columns appear in the file.
Enter a Filename or click the
Browse button to specify a measurement data file containing comma-separated, semicolon-separated, space-separated, and tab-separated columns of measurements. The files are typically CSV files (*.csv), data files (*.dat), or plain text files (*.txt).
Click the Add button (
) below the table to add an experimental parameter. Experimental parameters are useful for including additional parameters that represent model conditions for the experimental data and that are valid for the current experimental data file. In the
Name column, choose a parameter name from the global parameters defined in the model. Enter a global-scope expression or value in the
Expression column to assign a value to the parameter in this experiment. Use the
Load from File (

) and
Save to File (

) buttons to load and save experimental parameter names and expressions from and to a file. Use the
Delete button (

) to remove the selected parameter from the table.
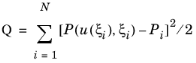 ,
,