
|
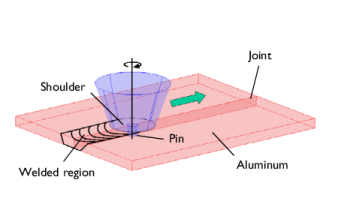

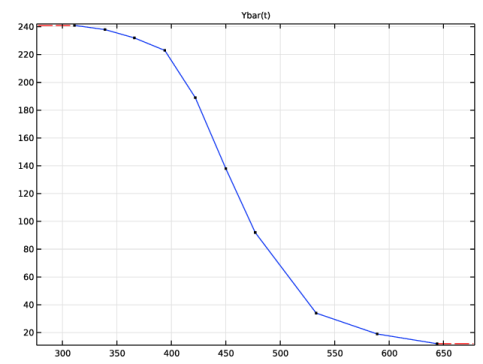
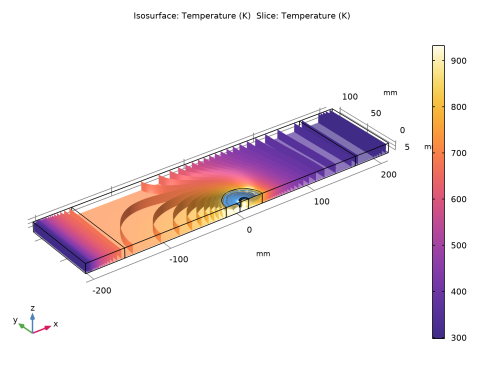
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Click Add.
|
|
4
|
Click
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
5
|
Click
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Select the object blk3 only.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
5
|
Locate the Variables section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
5
|
Locate the Variables section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1)>Heat Transfer in Solids (ht) click Initial Values 1.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
In the Settings window for Surface-to-Ambient Radiation, locate the Surface-to-Ambient Radiation section.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
In the tree, select Built-in>Aluminum.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
Click OK.
|
|
9
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|