The Generate Material Wizard contains the following steps:
Click the Next button (

) to proceed to the next step in the wizard.
Select the species to be included in the list. Use the Add All button (

) to add all species in the thermodynamic system. It is also possible to select a subset of the available species. In that case use the
Add Selected button (
) to add species. The
Selected species table is updated as you add species.
Notice that when using Generate Material for the Predefined System Water-steam this step is not included in the wizard.
Specify the mixture composition in terms of the Mole fractions or
Mass fractions of all species. The fractions should sum to one. This setting is only available for systems with more than one component, and for materials with more than one selected species.
Click the Next button (

) to proceed to the next step in the wizard.
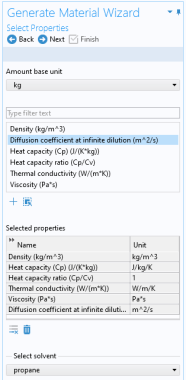
To add a property to the Selected properties list click the
Add Selected button (

). To remove properties, use the
Remove Selected button (
) or the
Remove All button (

)
When adding the Diffusion coefficient at infinite dilution, also select which of the species is the solvent. The material will include one diffusion coefficient for each of the remaining (solute) species.
For a gas phase material, the speed of sound c, and the isentropic compressibility
χf are also defined as
Click the Next button (

) to proceed to the next step.
Use the Component list to select where the Material will be added. The already existing components are shown in the top of the list. A new component can be created by selecting the desired space dimension. Select
Global at the end of the list to add the material under
Global Definitions. A global material can be utilized in any component, through the use of a Material Link. It can also be used to define phase specific properties when linked to a subnode of a
Porous Material.
Select Thermodynamics to base the material properties on functions in the current thermodynamic system. The required functions are created, if not already present, and added to the system. When evaluating material properties, the underlying thermodynamics functions are called.
Select Interpolation to generate interpolation functions for the material properties. In this case the required functions are first created and added to the system. Next, the functions are evaluated in a number of sampling points over a given range, for both temperature and pressure. The result of the evaluation is stored and used to define interpolation functions for all material properties.
For the Interpolation points, select
Same for all functions to use the same number of evaluation points for all functions. By selecting
Individual, the number of evaluation points can be given per function. The latter can for example be used to increase the number of points for a function that is known to vary faster than the rest of the functions.
Select one of the preset levels for the Maximum number of interpolation points. This is used to provide a maximum size of the underlying data for the interpolation functions. If the total number of evaluation points for any function, varying temperature and pressure, is exceeded, a warning is shown.
Define the temperature range and pressure ranges for the temperature and pressure by providing the Low and
High end values. To neglect the variation in either temperature or pressure, give the same value for the low and high end value. This can for example be used when the pressure variation is known to be negligible. For each range, also define the number of evaluation points in the
Number of points field. The underlying functions are evaluated at uniformly distributed positions across the temperature and pressure range.
When Individual has been selected for the
Interpolation points, the
Ranges and interpolation points can be specified per function to be created.
Click the Finish button (

) to create the specified Material and exit the wizard.
