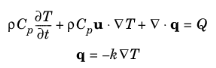
|
•
|
ρ (SI unit: kg/m3) is the alloy’s density.
|
|
•
|
Cp (SI unit: J/(kg·K)) is the alloy’s heat capacity at constant pressure.
|
|
•
|
k (SI unit: W/(m·K)) is the alloy’s thermal conductivity (a scalar or a tensor if the thermal conductivity is anisotropic).
|
|
•
|
u (SI unit: m/s) is the velocity field defined by the Moving Mesh node when parts of the model are moving in the material frame.
|
|
•
|
Q (SI unit: W/m3) is the heat source (or sink). Add one or more heat sources as separate physics features. See Heat Source node and Thermoelastic Damping subnode for example.
|
|
This model input does not override the Reference temperature Tref set in the Physical Model section of the physics interface, which is used to evaluate the reference enthalpy, and a reference density for incompressible nonisothermal flows.
|
|
•
|
Volume average (default), which calculates the effective conductivity of the alloy as the weighted arithmetic mean of austenite and martensite conductivities:
|
|
•
|
Reciprocal average, which calculates the effective conductivity of the alloy as the weighted harmonic mean of austenite and martensite conductivities:
|
|
•
|
Power law, which calculates the effective conductivity of the alloy as the weighted geometric mean of austenite and martensite conductivities:
|
|
When the material properties for the austenite and martensite phases are defined using the From material option, the properties are taken from Austenite phase and Martensite phase property groups respectively. If a property is not defined in these groups but is available in the Basic group, its definition is automatically synchronized. This mechanism is designed to make it possible to use two materials, one pure austenite material and one pure martensite material with properties defined in the basic group as an alternative to a single material with the properties defined in the Austenite phase and Martensite phase property groups. In that case, the two materials have to be selected instead of using the default Domain material option.
|