The Edit mixing rule dialog box is used to control the
mixing rules in the
material contents table of a
Multiphase Material or
Effective Material.
If there are several material properties in the table, you can step through the table without closing the dialog using the Previous Row (Discard Changes) (

),
Previous Row (Store Changes) (

),
Next Row (Discard Changes) (

), and
Next Row (Store Changes) (

) toolbar buttons. The current row of the is identified by the
Property Group and
Parameter fields.
where n is the number of phases,
Vf,i is the volume fraction of phase
i,
X is the effective material property, and
Xi is the material property of phase
i.
where wi is the mass fraction of phase
i,
Here, ρ is the effective density and
ρi is the density of phase
i.
where 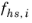 is the fraction used for phase i
is the fraction used for phase i,
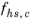
is the fraction corresponding to the constrained phase, and
lmix is a user-defined
mixing parameter (default: 0.8) defining the size of the transition zone between phases for the smooth Heaviside function
H.
In this section, the properties of the fiber reinforcements are denoted by subscript f, while properties of the matrix are denoted by
m. The mixing rules for composites are only available to a specific set of material properties. These rules should be used together with a Volume Averaged mixing rule for density.
The Halpin–Tsai model includes empirical factors ζ for the components of the elastic modulus and are a measure of the reinforcement that depends on fiber geometry. Some typical values for the orthotropic Young’s modulus are depicted in the table value. The value of
ζ for the components of
G is typically
1.
In the table above, l11 is the fiber length in the 11 direction,
w22 is the fiber width in the 22 direction, and
t33 is the fiber thickness in the 33 direction.
The bulk modulus of fiber, Kf, and matrix,
Km, under longitudinal strain are
The effective dynamic viscosity μ in suspensions may be modeled using the Krieger-type model as
When Krieger type viscosity is selected, enter a value or expression for the
Maximum packing concentration 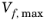
(dimensionless). The default is 0.62.