This postprocessing feature is used to estimate the deformation of a free surface from the pressure distribution on the boundary when using the Frozen Rotor or
Frozen Rotor with Initialization study types. When computing the flow field, a slip condition together with a constant pressure level
pext is applied on the boundary. The free surface deformation
ηFS is evaluated from the linearized free surface condition in a separate study step,
Stationary Free Surface, using the pressure from the Frozen Rotor study step:
Here, σ is the surface tension coefficient,
x =
x0 represents the position of the undisturbed surface (the feature selection), and
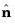
is its unit normal. The correct study sequence can be triggered by toggling the study window once a selection for the Stationary Free Surface feature has been made.
The Stationary Free Surface feature is supported by laminar and turbulent flow, and is applicable for small surface deformations (ηFS and its gradient should be small compared to the dimensions of the computational domain). If the surface deformation is large, a time-dependent study with a
Deforming Domain and a
Free Surface feature should be used instead.
Iterative solvers are necessary to reduce the cost of models with large number of degrees of freedom. The fluid flow interfaces use a Smoothed aggregation AMG solver per default. When the Stationary Free Surface feature is active and has a nonempty selection in a frozen rotor or stationary study step, a
Geometric multigrid solver is used instead to ensure robustness of the model.
Enter an External pressure pext corresponding to the average pressure level on the free surface.
Select the Include surface tension force in momentum equation check box to include the surface tension force in the momentum equation.
The Surface tension coefficient σ (SI unit: N/m) can be specified from predefined libraries, by selecting
Library coefficient, liquid/gas interface (the default) or
Library coefficient, liquid/liquid interface, or be set to
User defined.