You are viewing the documentation for an older COMSOL version. The latest version is
available here.
The available Boundary condition options for an inlet are
Velocity, Fully developed flow,
Mass flow, and
Pressure. After selecting a
Boundary Condition from the list, a section with the same or a similar name displays underneath. For example, if
Velocity is selected, a
Velocity section, where further settings are defined, is displayed.
The Normal inflow velocity is specified as
u =
−nU
0, where
n is the boundary normal pointing out of the domain and
U0 is the normal inflow speed.
The Velocity field option sets the velocity vector to
u =
u0. The components of the inlet velocity vector
u0 should be defined for this choice.
The Include synthetic turbulence option is available when the
Turbulence Model Type is set to
Large Eddy Simulation or
Detached Eddy Simulation. It is disabled by default. When it is enabled, the
Normal inflow velocity is specified as
u = −nU0 + u′in,t, and the
Velocity field option sets the velocity vector to
u = u0 + u′in,t, where
u′in,t is the fluctuating inlet velocity at time
t. The section titled
Turbulence Conditions controls the parameters that determine the fluctuating velocity.
|
•
|
For incompressible flow, the Pressure list has two options, Static and Total. For weakly compressible and compressible flow, the static pressure should be specified in the text field.
|
|
-
|
If Pressure is Static, and the reference pressure pref, defined at the physics interface level, is equal to 0, the value of the pressure p0, at the boundary, is the absolute pressure. Otherwise, p0 is the relative pressure at the boundary.
|
|
-
|
If Pressure is Total, the Average check box is available and cleared by default to prescribe the total pressure pointwise. If it is selected, the averaged total pressure is imposed in the weak forms instead.
|
When Include gravity is selected and
Use reduced pressure not selected in the interface
Physical model section, the
Compensate for hydrostatic pressure approximation (named
Compensate for hydrostatic pressure for incompressible flows) check box is available and selected by default. When it is selected, the hydrostatic pressure is automatically added to the pressure entered in
p0 user input.
|
•
|
The Suppress backflow option adjusts the inlet pressure locally in order to reduce the amount of fluid exiting the domain through the boundary. If you clear the suppress backflow option, the inlet boundary can become an outlet depending on the pressure field in the rest of the domain.
|
|
•
|
Flow direction controls in which direction the fluid enters the domain.
|
|
-
|
For Normal flow, it prescribes zero tangential velocity component.
|
|
-
|
For User defined, an Inflow velocity direction du (dimensionless) should be specified. The magnitude of du does not matter, only the direction. du must point into the domain.
|
The mass flow at an inlet can be specified by the Mass flow rate, the
Pointwise mass flux, the
Standard flow rate, or the
Standard flow rate (SCCM).
The Apply condition on each disjoint selection separately check box is selected per default. When this setting is selected, the mass flow condition is applied separately on each disjoint selection. If this option is not selected, the condition is applied over the whole feature selection. The
Apply condition on each disjoint selection separately should be disabled only if the flow conditions are known to be identical on each disjoint boundary.
The Mass flow rate option sets the integrated mass flow over the boundary selection, the
Normal mass flow rate to a specific value,
m. The mass flow is assumed to be parallel to the boundary normal, and the tangential flow velocity is set to zero.
For 2D components, the Channel thickness dbc is used to define the area across which the mass flow occurs. This setting is not applied to the whole model. Line or surface integrals of the mass flow over the boundary evaluated during postprocessing or used in integration coupling operators do not include this scaling automatically. Such results should be appropriately scaled when comparing them with the specified mass flow.
The Pointwise mass flux sets the mass flow parallel to the boundary normal. The tangential flow velocity is set to zero. The mass flux is a model input, which means that COMSOL Multiphysics can take its value from another physics interface when available. When
User defined is selected a value or function
Mf should be specified for the
Mass flux.
The Standard flow rate Qsv sets a standard volumetric flow rate, according to the SEMI standard E12-0303. The mass flow rate is specified as the volumetric flow rate of a gas at standard density — the
Mean molar mass Mn divided by a
Standard molar volume Vm (that is, the volume of one mole of a perfect gas at standard pressure and standard temperature). The flow occurs across the whole boundary in the direction of the boundary normal and is computed by a surface (3D) or line (2D) integral. The tangential flow velocity is set to zero.
For 2D components, the Channel thickness dbc is used to define the area across which the mass flow occurs. This setting is not applied to the whole model. Line or surface integrals of the mass flow over the boundary evaluated during postprocessing or used in integration coupling operators do not include this scaling automatically. Such results should be appropriately scaled when comparing them with the specified mass flow.
The Standard flow rate (SCCM) boundary condition is equivalent to the
Standard flow rate boundary condition, except that the flow rate is entered directly in SCCMs (standard cubic centimeters per minute) without the requirement to specify units. Here, the dimensionless
Number of SCCM units Qsccm should be specified.
The Fully developed flow option adds contributions to the inflow boundary, which force the flow toward the solution for a fully developed channel flow. The channel can be thought of as a virtual extrusion of the inlet cross section. The inlet boundary must hence be flat in order for the fully developed flow condition to work properly. In 2D axisymmetric models, the inlet normal must be parallel to the symmetry axis.
|
•
|
Flow rate, V0. Two-dimensional models also require an Entrance thickness, Dz, which is the out-of-plane thickness of the extruded entrance channel.
|
|
•
|
Average pressure, Pav. Note that Pav is the average pressure on the inflow boundary.
|
The Apply condition on each disjoint selection separately check box is selected per default. When this setting is selected, the fully developed flow condition is applied separately on each disjoint selection. If this option is not selected, the condition is applied over the whole feature selection. The
Apply condition on each disjoint selection separately should be disabled only if the flow conditions are known to be identical on each disjoint boundary.
The fully developed flow condition requires any volume force to be approximately aligned with the normal of the inlet boundary. The exception is gravity when the Include gravity setting is selected in the physics interface settings. Unless
Use reduced pressure is also selected, an option to
Compensate for hydrostatic pressure or
Compensate for hydrostatic pressure approximation becomes available. It is selected per default and should only be deselected if the inlet normal is aligned with the gravity force and you want to specify an average pressure that includes the hydrostatic pressure.
For the Turbulent Flow, Spalart-Allmaras interface, a value or expression for the
Undamped turbulent kinematic viscosity υ0 should be specified.
When Include transition modeling is selected in the SST turbulence model, the intermittency,
γ, is set to
1. For the v2-f turbulence model, the additional choice between
Isotropic turbulence and
Specify turbulence anisotropy appears. For
Specify turbulence anisotropy, a value for the turbulent relative fluctuations at the inlet,
ζ0, may be specified. When
Specify turbulence variables is selected, values or expressions for the dependent turbulence variables should be defined. Availability is based on the physics interface and the boundary condition chosen.
For the Large Eddy Simulation and Detached Eddy Simulation interfaces, when the Include synthetic turbulence option is selected, the
Number of Fourier modes is specified as an integer value greater than or equal to 2 in order to control the number of Fourier modes used in the generation of the fluctuating inlet velocity.
When the Use random seed check box is enabled, one can specify the value of a
Random seed,
r, which is used in randomly generating various angles that determine the orientation of the fluctuating velocity.
The Turbulent intensity IT and
Turbulence length scale LT values are related to the turbulence variables via the following equations,
Equation 3-2 for the
Inlet and
Equation 3-3 for the
Open Boundary:
(3-2) Inlet 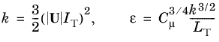
(3-3) Open Boundary 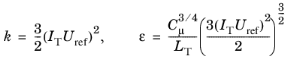
For the Open Boundary and
Boundary Stress options, and with any Turbulent Flow interface, inlet conditions for the turbulence variables also need to be specified. These conditions are used on the parts of the boundary where
u ⋅ n < 0, that is, where flow enters the computational domain.
For the k-ω and
SST turbulence models the
Turbulent intensity IT and
Turbulence length scale LT values are related to the turbulence variables via the following equations,
Equation 3-4 for the Inlet and
Equation 3-5 for the Open Boundary:
(3-4) Inlet 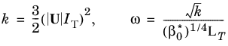
(3-5) Open Boundary 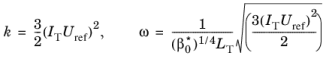
For the inlet, IT and
LT can be chosen in the lists. There are:
|
•
|
Two options for LT: Geometry based, and User defined. In the Geometry based option, it is automatically computed based on 7% of the hydraulic diameter.
|
This section is displayed by clicking the Show button (

) and selecting
Advanced Physics Options.