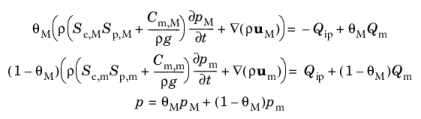Use the Unsaturated Dual Permeability Medium feature to model the transport in an unsaturated dual permeability medium where the Richards’ Equation (
Equation 7-4) describes the transport in each system.
θM is the volume fraction of the macropores,
Qip is the interporosity flow which is the mass transfer from the macroscale to the microscale system. The indices
M and
m stand for macropores and micropores, respectively.
The feature has three default subfeatures —the Fluid subfeature where the fluid density
ρ (SI unit: kg/m
3) and dynamic viscosity
μ (SI unit: Pa·s) are defined, the
Macropores subfeature where the hydraulic properties of the macroporous matrix are defined, and the
Micropores where the hydraulic properties of the microporous matrix are defined.
Select a coordinate system from the Coordinate system list for the interpretation of directions in anisotropic material properties. The default is the
Global coordinate system, and the list contains any additional orthonormal coordinate system (except boundary coordinate systems) added under the
Definitions node.
The subnodes inherit these coordinate system settings. In particular, the Permeability or
Hydraulic conductivity (in the
Macropores and
Micropores subnodes) should be set according to the coordinate system selected in this section.
With this option, define the first term in Equation 7-7. Therefore, choose from a drop-down menu one of the following formulations:
If From retention model is chosen, the first term of
Equation 7-7 accounts only for the specific moisture capacity
Cm,i which is defined by the
Retention Model in the
Macropores (
i=M) or
Micropores (
i=m) subnode:
From liquid content enforces the first term of
Equation 7-7 to be defined in terms of liquid volume fraction as
Specify the Fluid Transfer Function αw which is used to calculate the interporosity flow, which is the mass exchange between macro- and microscale system:
with pM being the pressure within the macroscale system and
pm the pressure within the microscale system.