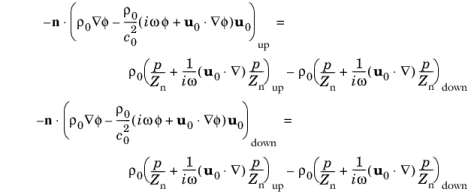Use the Interior Impedance or
Pair Impedance node in a frequency domain analysis to define the specific transfer impedance at the boundary between two domains or parts in an assembly as the ratio of pressure drop to normal velocity
Zn = Δp/(n ·
u). The formulation is following the so-called Ingard-Myers condition. The associated boundary condition is