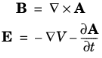The defining equation for the magnetic vector potential is a direct consequence of the magnetic Gauss’ law. The electric potential results from Faraday’s law. In the magnetostatic case where there are no currents present, Maxwell–Ampère’s law reduces to
∇ × H = 0. When this holds, it is also possible to define a magnetic scalar potential by the relation
H = −∇Vm.