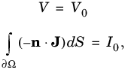The Floating Potential node is used when modeling a metallic electrode at floating potential. It applies a constant voltage
V0 on the boundary (for domain features, this is the boundary enclosing the selected domain), such that the total normal electric current density
J equals a specific current
I0:
where Ω represents the boundary and
n refers to the surface normal. The constant boundary voltage implies the tangential electric field equals zero; the electric field will be perpendicular to the boundary:
In case of I0 = 0 (the default case), the boundary will behave as an unconnected perfect conductor (a floating equipotential). This is a good approximation when the conductivity of the electrode is many orders of magnitude larger than that of the surrounding medium. Although locally the current density may vary, the total current entering or leaving the boundary equals zero.
If the floating potential touches a point, boundary, or domain feature that is not floating (a Terminal or
Ground feature), the floating potential will acquire that feature's potential. If the floating potential is set to a certain current, or connected to a circuit, it behaves like a terminal.
The Harmonic Perturbation subnode (it is of the exclusive type) is available from the context menu (right-click the parent node) or in the
Physics toolbar, click the
Attributes menu and select
Harmonic Perturbation. For more information see
Harmonic Perturbation — Exclusive and Contributing Nodes in the
COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual.
The Floating potential identifier text area shows the unique identifier for the floating potential feature. It is used to identify the global variables created by the node, such as the voltage. The Floating potential group check box in the
Settings window for
Floating Potential controls how potentials are assigned to boundary segments in the feature’s boundary selection. If this check box is not selected, a single potential is applied to all boundaries in the selection. If the check box is selected, each group of contiguous boundaries in the selection is given a unique potential. This simplifies the setup of models with many floating electrodes. The values of the potential at each group of boundaries are then made available in postprocessing, collected in a vector variable.
The following options are not available if the Floating potential group check box is selected. Select a specification for the
Floating potential current — choose
User defined (the default) to specify a total
Current I0 (SI unit: A) that flows from the electrode. The default is 0 A, corresponding to an unconnected electrode. Select
Circuit to connect the floating potential to an Electrical Circuit interface.
Enter an Initial value for voltage Vinit (SI unit: V). The default is 0 V.