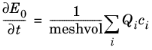The fluence rate E0 (SI unit: W/m
2) is a volume quantity that indicates potential exposure to radiation. The fluence rate at any point in a domain is the total incident power that would hit a small spherical target at that location, from all directions, divided by the cross sectional area of the sphere (
Ref. 16).
In the path of a collimated beam of uniform intensity I (SI unit: W/m
2), the fluence rate is simply
I; however, the fluence rate distribution may be more complicated if there are multiple beams intersecting at a point (since fluence rate takes contributions from radiation arriving in all directions), or if the radiation is diffusely emitted or reflected.
The Fluence Rate Calculation node is a special type of
Accumulator (Domain) that can be added to a model when the ray power is solved for, meaning that one of the options
Compute power,
Compute intensity and power, or
Compute intensity and power in graded media should be selected from the physics interface
Intensity Computation list. This feature defines an accumulated variable in each domain mesh element that gets the following contribution from rays as they propagate through the element:
where the sum is taken over the rays within each mesh element, Qi (SI unit: W) is the ray power, and
ci (SI unit: m/s) is the speed of light of the ray. The division by the mesh element volume
meshvol compensates for the tendency of a larger domain element to intersect a greater number of rays. Rather than a time integral, the above can be thought of as a path integral of ray power from the entrance point to the exit point as each ray traverses the mesh element.