where p is the percolation exponent.
where m,
n are scalars that can be set to arbitrary values and
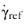
denotes a reference shear rate where
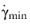
is a lower limit for the evaluation of the shear rate magnitude. The temperature and conversion dependent Power law viscosity becomes
where τtr is the critical stress,
μ0 is the zero shear rate viscosity,
μ∞ is the infinite shear-rate viscosity, and
n is a dimensionless parameter.
where Q denotes the activation energy,
R is the universal gas constant, and
T and
T0 are the temperature and reference temperature, respectively.
where C1WLF and
C2WLF are model constants, and
TWLF is the reference temperature.
where b denotes a temperature sensitivity, and
T0 is the reference temperature.
Viscosity factor calculated using Equation 9-2 or
Equation 9-3 can be used together with the non-Newtonian inelastic models included in the fluid flow interfaces. The models are defined in the fluid flow interfaces and provide a complete model for the apparent viscosity that is temperature and shear-rate dependent.