The evolution of the degree of cure or conversion cr is described by the convection equation with a source term:
where nr is the polynomial order and
kr is a temperature-dependent reaction rate constant that follows an Arrhenius equation
where Q is the activation energy and
k0 is the frequency factor.
Kamal–Sourour is a combination of the nth order and Sestak–Berggren models
where k1 and
k2 are temperature-dependent reaction rate constants
where Q1,2 are the activation energies and
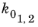
the frequency factors.
where 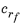 ,
, 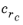 , Cf
, Cf, and
Cd are the model parameters.